In the realm of food science and quality control, the determination of Solid Fat Content (SFC) is a critical parameter that influences the application and performance of fats and oils. Traditional methods of SFC measurement, such as the dilatometric method, have been fraught with inefficiencies and inaccuracies. However, the advent of Low-Field Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (LF-NMR) has revolutionized the way SFC is measured, offering a swift and precise alternative.

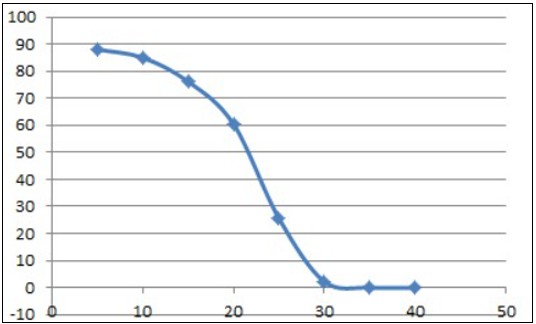
The concept of SFC is straightforward yet significant; it refers to the proportion of fat that is solid at a given temperature. This attribute is pivotal in defining the usability and versatility of fats in various food products. The relationship between SFC and temperature dictates the product’s range of applications, making it an essential quality control metric.
LF-NMR has emerged as the preferred method for SFC measurement due to its inherent advantages over traditional techniques. The process is based on the distinct characteristics of hydrogen protons in solid and liquid fats within a magnetic field. Solid fat protons exhibit rapid signal decay in the NMR Free Induction Decay (FID) signal, often reaching zero within microseconds, whereas liquid fat protons decay more slowly, with minimal loss at the same time scale.

The direct method of LF-NMR measurement involves capturing the FID signal of the sample, distinguishing between solid and liquid signals, and directly quantifying the SFC. The stark difference in signal decay rates between solid and liquid components allows for accurate measurement by selecting appropriate points in the FID signal.
The implementation of LF-NMR in SFC measurement is not only limited to its accuracy and speed but also extends to its user-friendly nature. The process does not require highly skilled operators, reducing the margin for human error and enhancing overall efficiency.
For those seeking to incorporate LF-NMR technology into their quality control processes, instruments such as the PQ001-SFC Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Solid Fat Content Analyzer are recommended. These devices are designed to provide reliable SFC measurements, ensuring product consistency and compliance with industry standards.
The integration of LF-NMR in the measurement of Solid Fat Content represents a significant leap forward in food science and quality assurance. By offering a rapid, accurate, and efficient method to determine SFC, LF-NMR technology empowers manufacturers to maintain high-quality standards and meet consumer expectations. As the food industry continues to evolve, the adoption of LF-NMR for SFC measurement is set to become increasingly prevalent, underpinning the drive for excellence in product development and quality control.
Keywords: Solid Fat Content, SFC, Low-Field Nuclear Magnetic Resonance, LF-NMR, food science, quality control, dilatometric method, FID signal, PQ001-SFC, product consistency, industry standards.
 NIUMAG
NIUMAG