Low-field Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (LF-NMR) technology is a powerful tool that has been increasingly utilized in the study of moisture migration during the drying process of food materials. This non-invasive and analytical technique provides insights into the dynamics of water within food substances, which is crucial for optimizing drying conditions and ensuring food quality.
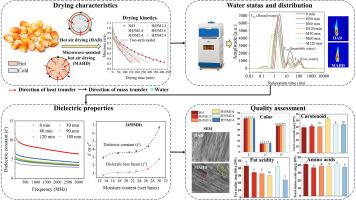
In the context of food drying, LF-NMR is particularly valuable for examining the behavior of both free and bound water. Free water, which is not strongly associated with food molecules, can be easily removed during drying. In contrast, bound water is more tightly held and requires more energy to remove. The ability of LF-NMR to distinguish between these two states of water allows for a better understanding of the drying process and the impact on food texture, rehydration properties, and overall quality.
The application of LF-NMR in food drying research has been highlighted in various studies. For instance, one study used LF-NMR T2 relaxometry to investigate the transportation mechanisms of free and bound water during drying, revealing that cell membranes rupture at different stages of drying, depending on the penetration rate of heat energy and the pressure gradient between intracellular and intercellular environments . This information is vital for developing more efficient drying methods that can preserve the nutritional and sensory qualities of food.
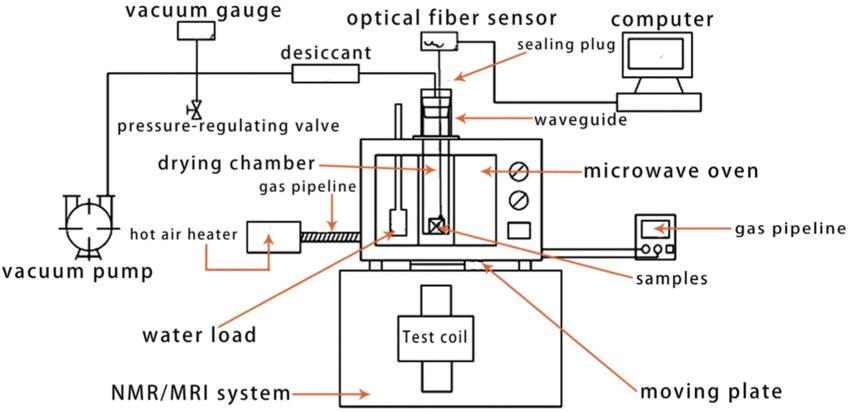
Moreover, LF-NMR can be used to monitor the moisture distribution within food materials in real-time, providing a means to assess the uniformity of the drying process. This capability is particularly useful for industries that rely on precise control of moisture content for product quality and shelf life, such as in the production of dried fruits, vegetables, and grains.
In addition to its role in research, LF-NMR has potential applications in the quality control of dried foods. By establishing a baseline for moisture migration and water state, LF-NMR can help ensure that food products meet safety and quality standards.
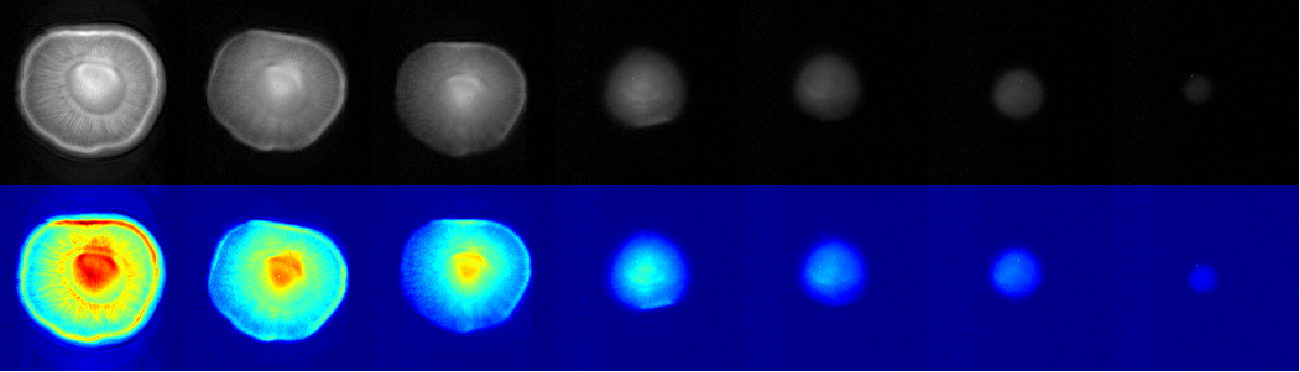
In conclusion, LF-NMR is a versatile technology that offers significant benefits for the study and optimization of moisture migration during food drying. Its ability to provide detailed information on the water state within food materials makes it an invaluable tool for researchers and industry professionals alike. As the technology continues to advance, its applications in the field of food science are expected to expand, contributing to improvements in food processing and quality assurance.
 NIUMAG
NIUMAG