Benchtop NMR Medical Imaging MRI Teaching Experiment
The uniformity of the magnetic field is very critical to MRI. This article briefly introduces the shimming method of Benchtop NMR.
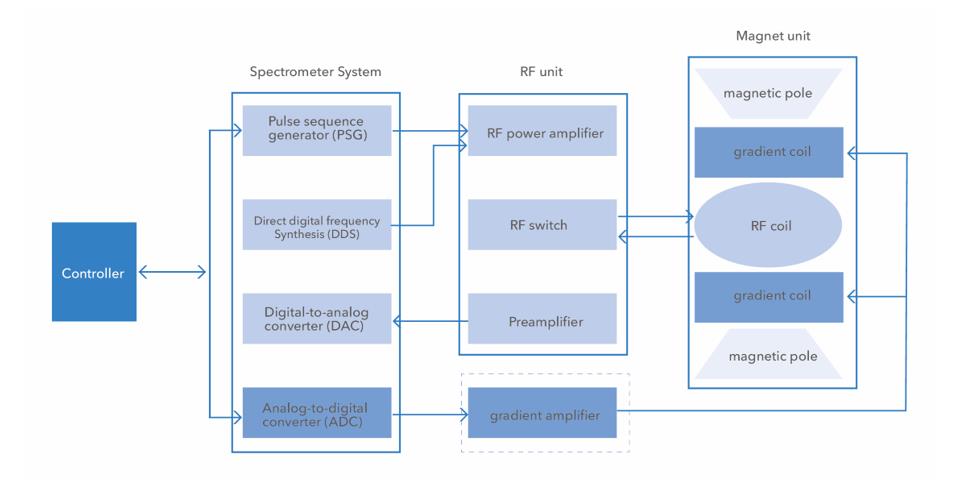
Benchtop NMR System Architecture Diagram
The uniformity of the magnetic field refers to the identity of the magnetic field within a specific volume limit, that is, whether the number of magnetic lines of force passing through a unit area is the same. In magnetic resonance systems, homogeneity is measured in parts per million (ppm) of the main magnetic field as a unit of deviation. For different main magnetic field sizes, the deviation units are also different. For example, for 1.0T magnetic resonance, 1 ppm deviation unit is converted to H proton frequency and is calculated to be about 42MHz.
The uniformity of the main magnetic field directly affects the T2* relaxation time of the tissue. When the uniformity of the main magnetic field is worse, that is, the shorter the T2*, the faster the relaxation, which is reflected from the magnetic resonance signal, that is, the shorter the tail of the FID signal. When the homogeneity of the main magnetic field is higher, that is, the longer T2* is, the slower the relaxation is, that is, the longer the tail of the FID signal is. Theoretically, when the main magnetic field is absolutely uniform, T2*=T2, the FID decays with the intrinsic 2 relaxation of the tissue.
Influence of main magnetic field inhomogeneity on T2
Influence of main magnetic field inhomogeneity on T2
When the Benchtop NMR collects signals, it adjusts the parallelism of the two magnetic poles by observing the decay speed of the nuclear magnetic resonance FID signal on the display (that is, the length of the FID tail), so as to achieve the purpose of adjusting the uniformity of the main magnetic field. When the tail of the FID signal is longer, that is, the FID attenuation envelope is slower, it means that the uniformity of the magnetic field is higher.
The uniformity of the main magnetic field of the permanent magnet MRI is related to the parallelism between the magnetic poles, so we can directly adjust the parallelism of the two magnetic poles to achieve the purpose of shimming; the magnetic field uniformity achieved by adjusting the parallelism of the magnetic poles is also It cannot fully meet the needs of MRI, so other methods of shimming are also required, mainly including passive shimming and active shimming.
Passive shimming is to stick small magnetic sheets or magnetic steel sheets on the inner and outer surfaces of the magnetic poles, and adjust the uniformity of the magnetic field by changing the local magnetic lines of force by the small magnetic sheets or magnetic steel sheets. In this experimental device, the uniformity between the magnetic poles is better. , so the passive shimming method is not used. The small magnetic piece in the physical picture below is the passive shimming method.
The active shimming method is mainly based on the fact that the energized coil will generate a magnetic field around the coil, and the inhomogeneity of the main magnetic field is corrected by applying a small magnetic field generated by appropriate current to the coils in different directions.
 NIUMAG
NIUMAG