Low-field NMR applied to the measurement of oil and moisture content in coffee beans
Coffee beans refer to the fruit of plants used to make coffee. The oil content and water content of coffee beans determine the taste of coffee. Different roasted coffee beans will result in different tastes of coffee. How to tell if coffee beans are roasted properly? It is very important to detect the oil and moisture content of coffee beans.
Low field NMR can do many for Coffee beans quality control
Oil moisture content, T2, imaging test of different roasted coffee beans by NMR instrument.
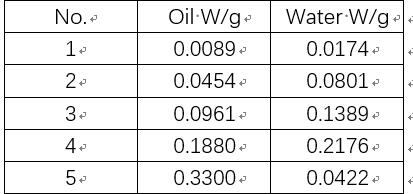
Table 1 The mass of the sample weighed for calibration
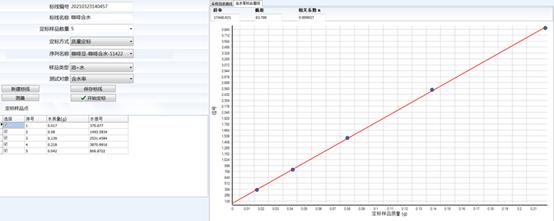
Calibration of Oil samples
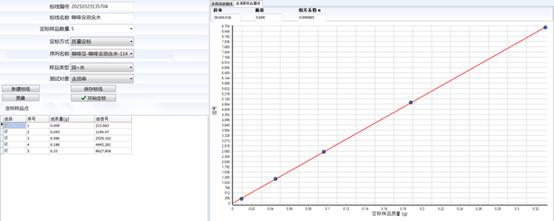
Calibration line of water sample
The above two pictures are the calibration results of soybean oil and aqueous solution when testing the oil-containing water content, and the correlation coefficient of the obtained marking line is above 0.999.
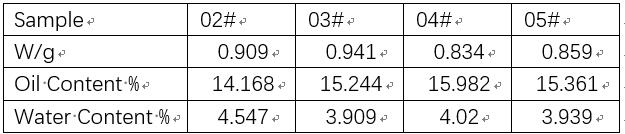
Table 2: NMR instrument test result of coffee beans
The above table 2 shows the results of oil and moisture content obtained by different roasted coffee beans. The 02# sample was not roasted, and the 03#, 04# and 05# samples were roasted to different degrees. From the test results, the 02# sample the oil content is lower than the oil content after baking, but the water content is higher.
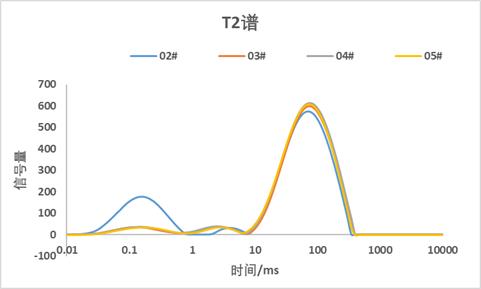
Fig.4 T2 spectrum of each sample
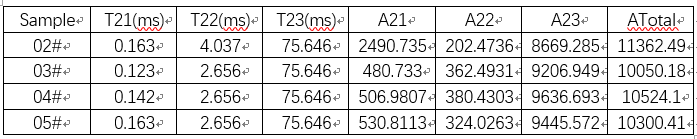
Table 3 T2 relaxation value of each sample
Figure 4 and Table 3 above are the results of the quality normalization of the test data of each sample; it is drawn from the figure that after baking, the strongly bound water peak drops significantly, and the T22 relaxation moves to the left; 02# total peak The area is larger than the other three samples.
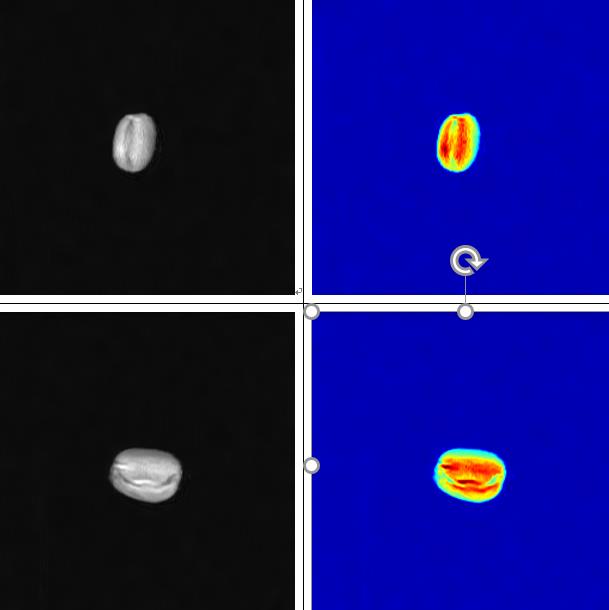
The above is an imaging image of 1 grain of each of the 2 samples, which shows the distribution of oils and fats in coffee beans.
Conclusion
Low-field nuclear magnetic resonance analysis technology can be used to detect the oil-water content of coffee beans, T2 distribution and imaging tests.
 NIUMAG
NIUMAG