Low field NMR Study on Seed Germination Process
Seed Germination Process
The seed germination process is divided into 4 steps: imbibition, water and enzyme activation, seed embryos break through the seed coat, and grow into seedlings.
- Imbibition: soak the seeds in water or the seeds in moist soil, the hydrophilic substances in the seeds will absorb water molecules, which will increase the volume of the seeds rapidly. , and then gradually slows down. As a result of imbibition, the seed coat becomes soft or cracked, and the permeability of the seed coat to gas increases, which promotes seed germination.
- Hydration and Enzyme Activation: When the water absorption stage of the seed is over, the cell wall of the seed will be hydrated with the protoplasm, various enzymes in the seed will also start to activate, and the respiration and metabolism will increase sharply.
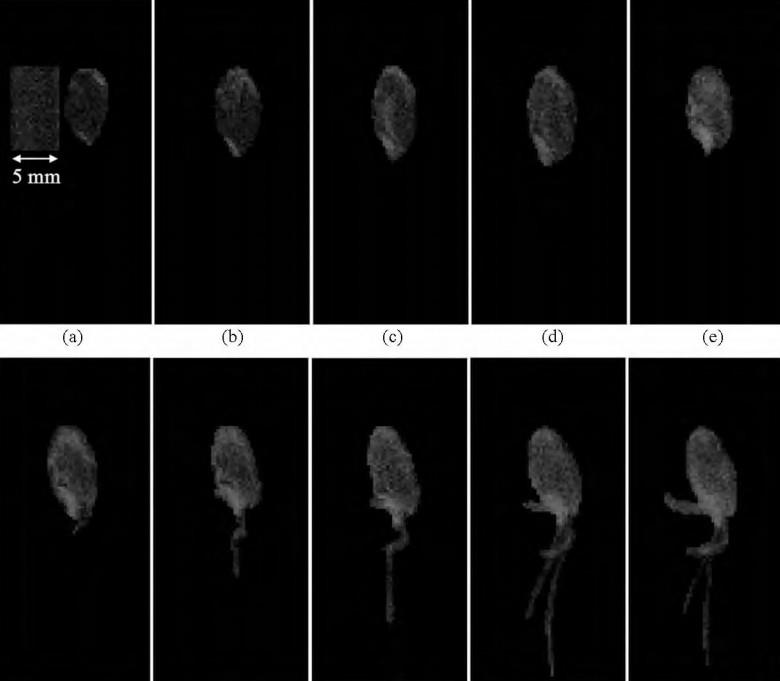
- The seed embryo breaks through the seed coat: the seed embryo will break through the seed coat, and then the volume will increase. Most of the seeds of the public first grow the radicle, and then grow the embryo.
- Grow into seedlings: The seeds grow radicle, and after the germ, roots, stems and leaves gradually grow to form seedlings.
Conditions Required For Seed Germination
- Appropriate moisture: First, during the germination of seeds, the transport of nutrients stored in the cotyledons or endosperm and the process of cell division require moisture; Bean) germination requires more water than grass seeds (wheat); third, in agricultural production, seed soaking can be performed to meet the water demand for seed germination.
- Adequate air: mainly oxygen. After the seeds absorb sufficient water, they must have sufficient oxygen, and the nutrients stored in the embryo and endosperm can produce intermediate products and energy through respiration to meet the needs of germination. Generally, seeds can germinate normally when the oxygen content in the air is more than 10%, and seeds with more fat need more oxygen than seeds with more starch; when the oxygen content drops below 5%, most seeds cannot germinate.
- Appropriate temperature: Appropriate temperature is a necessary condition for normal life activities. If the temperature is too high or too low, seeds cannot germinate normally.
Low Field NMR Exploring the Water Required for Seed G ermination
Water is an essential reaction substrate and medium in the physiological and metabolic activities of seeds. The entire process of seed germination is closely related to the content and distribution of its internal water. Too much or too little water will have adverse effects on seed germination and growth. Therefore, during germination The water absorption of seeds and the changing laws of water content play an important guiding role in their germination.
Determining the moisture in seeds is mainly to analyze the changes in moisture by drying or dissecting the seeds to observe their structure. Both are destructive and cannot continuously and accurately measure the moisture changes of the same batch of seeds, and either can only be used. Obtaining information on moisture content does not give information on internal moisture changes.
Low Field nuclear magnetic resonance (Low Field NMR) technology has the advantages of non-destructive and non-invasive technology, and has great potential in the visual detection of seed moisture, which can reveal the changing laws of moisture content and distribution in seeds from the microscopic level. It helps to accurately determine the germination and emergence ability of seeds, so as to provide a basis for establishing a good growth state of crops and seeking appropriate drought resistance countermeasures.
 NIUMAG
NIUMAG