About magnetic resonance rapid detection technology
Magnetic resonance rapid detection technology
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) is a cross-cutting technique for rapid detection of biological samples, also known as magnetic relaxation switching (MRSw) technology. The technology, which combines nanotechnology, immune technology and magnetic resonance technology, was first discovered by the Weissleder team in 2001.At the same time, the team designed four models, including DNA-DNA, protein-protein, protein-small analysis and enzyme catalysis, which were published in NATURE in 2002.
Principle of magnetic resonance detection
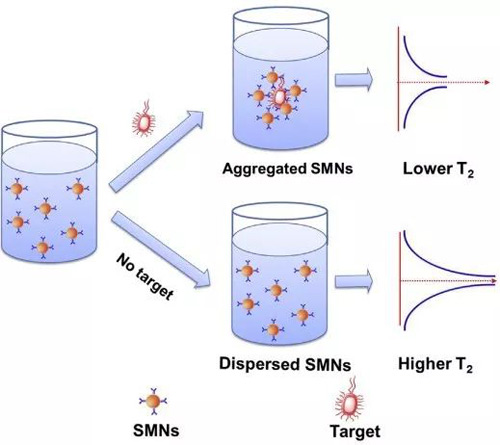
The surface of nanometer/micron magnetic beads contains many groups, such as -COOH, -OH, -OCH3, which can be combined with biological ligands by chemical/physical means to prepare sensor probes, to specifically identify target objects. In the presence of the target, the interaction between the target and the probe changes the particle from the dispersed state to the aggregated state, resulting in the change of the transverse relaxation time (T2) of the water molecule. Therefore, the target can be detected according to the change of T2.
As shown in the figure below, when the nanoprobe detects salmonella duck, when the target bacteria is present, the nanoparticles gather and the solution presents a low transverse relaxation time (T2).In the absence of the target bacteria, the nanoparticles remained in their original state and the solution showed a higher transverse relaxation time (T2).
Nanotechnology, immune technology, magnetic resonance technology in this method
Nanotechnology

Nanomaterials are materials that have at least one dimension at nanoscale size (0.1-100nm) or are composed of them as basic units in three-dimensional space Rock Core NMR system. It has many effects different from conventional materials, such as quantum effect, macroscopic quantum tunneling effect, surface effect, and small-size effect. Magnetic nanoparticles also exhibit paramagnetism or superparamagnetism. Paramagnetism or towards paramagnetism is the presence of external magnetic field, the nanoparticles will show magnetism, when the external magnetic field removed, the net magnetic moment of the nanoparticles is zero, that is, the external magnetic field does not show magnetism. At the same time, in the external magnetic field, each magnetic nanoparticle produces a large magnetic dipole, and the resulting local magnetic gradient causes the heterogeneity of the external magnetic field. When water molecules pass through this non-uniform magnetic field, their protons accelerate the relaxation, causing a change in the longitudinal relaxation time (T1)/the transverse relaxation time (T2).
Immune
technology
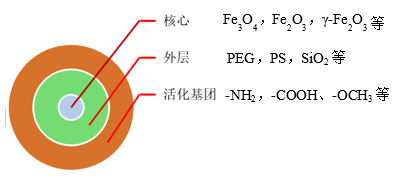
The above two pictures are the “core-shell” model of nanometer magnetic beads and the common covalent modification in magnetic bead modification. The core of the magnetic bead is a magnetic material, such as material -Fe2O3, Fe3O4, Fe2O3.The outer layer is made of polystyrene, polyethylenimine or polyacrylic acid and other high polymer materials to ensure good magnetic sealing, not easy to appear magnetic leakage phenomenon. The activated groups on the surface include carboxyl group, amino group, thiol group, toluene sulfonyl group and epoxy group, which can be combined with biological ligands (antibodies, DNA, RNA, etc.) through chemical/physical action.
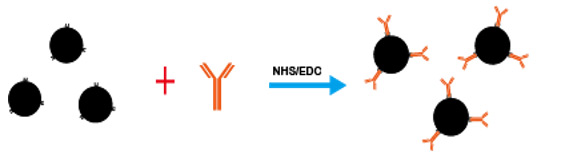
Biological modification of magnetic nanoparticles is the premise of specific detection of magnetic resonance technology. Biological modification of magnetic nanoparticles can be divided into direct modification and indirect modification. Direct modification is divided into physical adsorption and covalent coupling. Physical adsorption refers to hydrophobicity and electrostatic interaction between bioaffinity molecules such as proteins and nanomaterials. Covalent coupling refers to the modification of sulfides, amino groups or carboxyl groups on the surface of nanoparticles, and the formation of covalent bonds between these groups and bioaffinity molecules to achieve the biological modification of nanoparticles, while indirect modification requires the mediation of streptavidin.
Magnetic resonance technique

When the object exists, the object interacts with the probe, and the magnetic bead changes from a dispersed state to an aggregated state, resulting in the non-uniformity of the external magnetic field. When water particles pass through this non-uniform magnetic field, their protons accelerate relaxation, causing a change in transverse relaxation time (T2) that can be quantified by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR/MRI).
 NIUMAG
NIUMAG