Moisture Migration of Food
Moisture Migration Background
Moisture migration refers to the movement of moisture or water vapor from areas of high moisture content to areas of low moisture content. This process can occur in various materials, including building materials, foods, and pharmaceuticals.
In building construction, moisture migration is a critical consideration to prevent moisture-related problems, such as mold growth, decay, and structural damage. Moisture can migrate through walls, roofs, and floors due to various factors, such as air movement, temperature gradients, and vapor pressure differences. To control moisture migration, builders use various moisture management strategies, such as vapor barriers, insulation, and proper ventilation.
In the food industry, moisture migration can affect the quality, texture, and shelf life of products. For instance, moisture migration can cause crispy foods to become soggy, or cause the formation of ice crystals in frozen foods. Food manufacturers use various techniques, such as packaging, refrigeration, and drying, to manage moisture migration and maintain the quality of their products.
In the pharmaceutical industry, moisture migration can affect the stability and efficacy of drugs. Moisture can degrade the chemical composition of drugs and reduce their potency. To prevent moisture migration in pharmaceuticals, drug manufacturers use various techniques, such as desiccants, moisture barriers, and proper storage conditions.
Moisture Migration Measurement Methods
There are several test methods available for determining moisture migration in various materials. The specific method chosen will depend on the material being tested and the desired accuracy of the measurement. Here are some common methods for testing moisture migration:
ASTM E96-16 Standard Test Method for Water Vapor Transmission of Materials: This test method is used to measure the water vapor transmission rate (WVTR) of materials. The WVTR is the amount of water vapor that passes through a material over a specified period of time. This test method is commonly used in the construction industry to evaluate the effectiveness of vapor barriers and other moisture control strategies.
ASTM F1249-13 Standard Test Method for Water Vapor Transmission Rate Through Plastic Film and Sheeting Using a Modulated Infrared Sensor: This test method is used to measure the WVTR of plastic films and sheeting. It uses a modulated infrared sensor to measure the water vapor transmission rate through the material. This test method is commonly used in the food packaging industry to evaluate the effectiveness of packaging materials in preventing moisture migration.
Karl Fischer Titration: This method is used to determine the moisture content of a sample by measuring the amount of water that reacts with a Karl Fischer reagent. This method is commonly used in the pharmaceutical industry to determine the moisture content of drugs and other pharmaceutical products.
Calcium Carbide Method: This method is used to determine the moisture content of soil. It involves reacting soil samples with calcium carbide, which generates acetylene gas. The amount of gas generated is proportional to the moisture content of the soil.
Gravimetric Method: This method involves weighing a sample of the material before and after it is exposed to a controlled environment with known temperature and humidity. The difference in weight is used to calculate the amount of moisture that has migrated through the material. This method is commonly used in the construction industry to evaluate the moisture resistance of building materials.
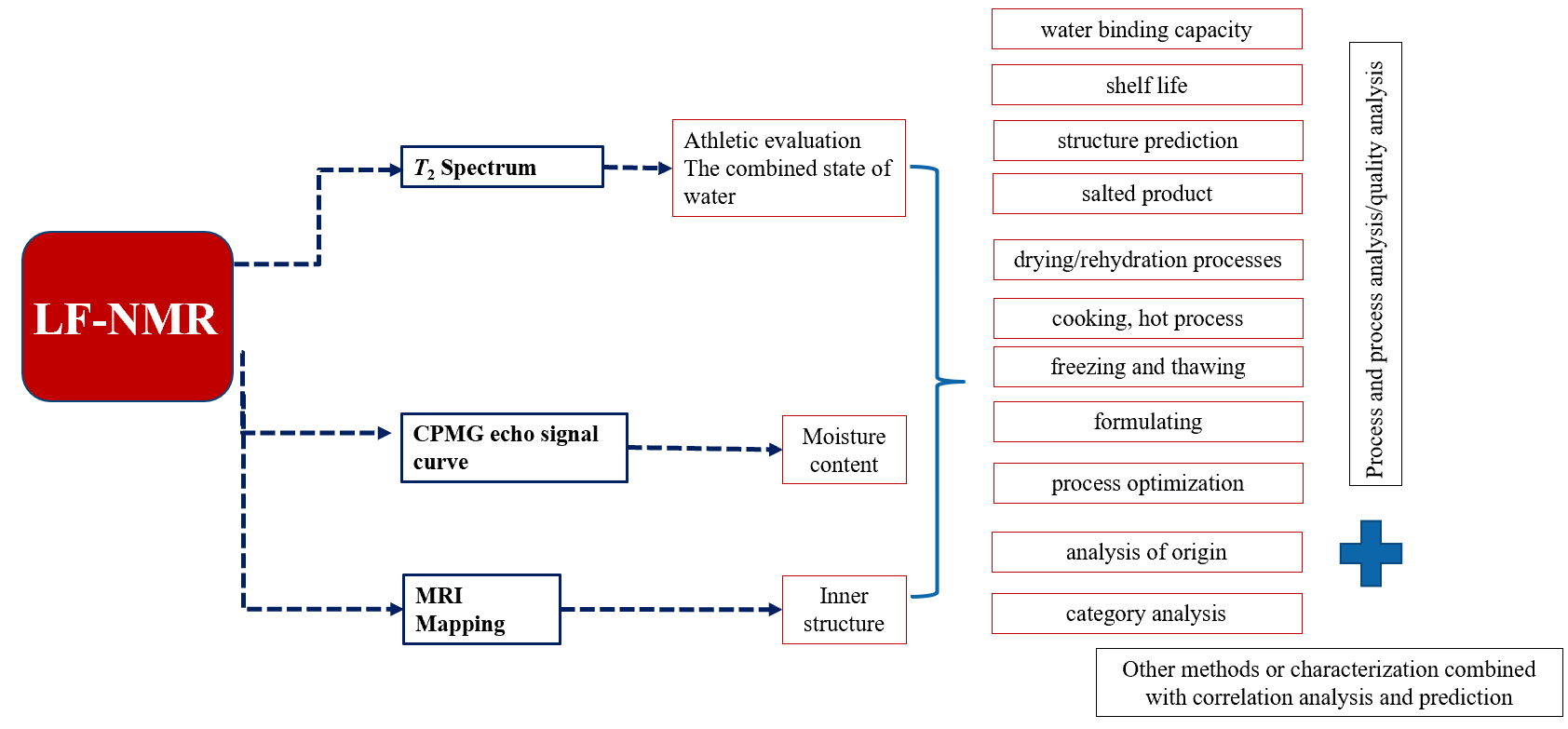
Moisture Migration Measured by Low Field NMR
Low field nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) is a non-destructive method that can be used to determine moisture migration in various materials. This technique is based on the principle that water molecules have a magnetic moment and can be excited by a radiofrequency pulse in the presence of a magnetic field.
Low field NMR can be used to determine several moisture-related parameters, including:
T2 relaxation time: The T2 relaxation time is a measure of the rate at which water molecules lose their energy and return to their original state. Moisture migration can affect the T2 relaxation time of a material, making it a useful parameter for evaluating moisture content and distribution.
Bound and free water content: Low field NMR can distinguish between bound water, which is tightly bound to a material, and free water, which is more mobile. This information can provide insights into the moisture migration behavior of a material.
Pore size distribution: Moisture migration can affect the pore size distribution of a material, which can be determined using low field NMR. This information can be useful in evaluating the moisture resistance of building materials, such as concrete.
Advantages of Moisture Migration Measured by Low Field NMR
Low field NMR has several advantages over other moisture migration test methods. It is non-destructive, fast, and requires minimal sample preparation. It can also provide detailed information about the moisture content and distribution in a material, which can be useful for quality control and product development purposes.
Non-destructive: Low field NMR is a non-destructive method that can measure moisture migration without damaging the sample. This makes it ideal for testing expensive or delicate materials, such as pharmaceuticals or cultural artifacts.
Fast: Low field NMR can provide moisture migration data quickly, often in a matter of minutes. This is faster than other methods, such as gravimetric testing, which can take hours or days.
High sensitivity: Low field NMR is highly sensitive to water molecules, which makes it an effective method for detecting small amounts of moisture migration. This can be particularly useful in evaluating the moisture resistance of building materials or the stability of pharmaceuticals.
Detailed information: Low field NMR can provide detailed information about the moisture content and distribution in a material. It can distinguish between bound and free water and provide insights into the pore size distribution of a material. This information can be useful for quality control and product development purposes.
Versatile: Low field NMR can be used to test a wide range of materials, including building materials, foods, and pharmaceuticals. This versatility makes it a valuable tool for researchers and manufacturers in various industries.
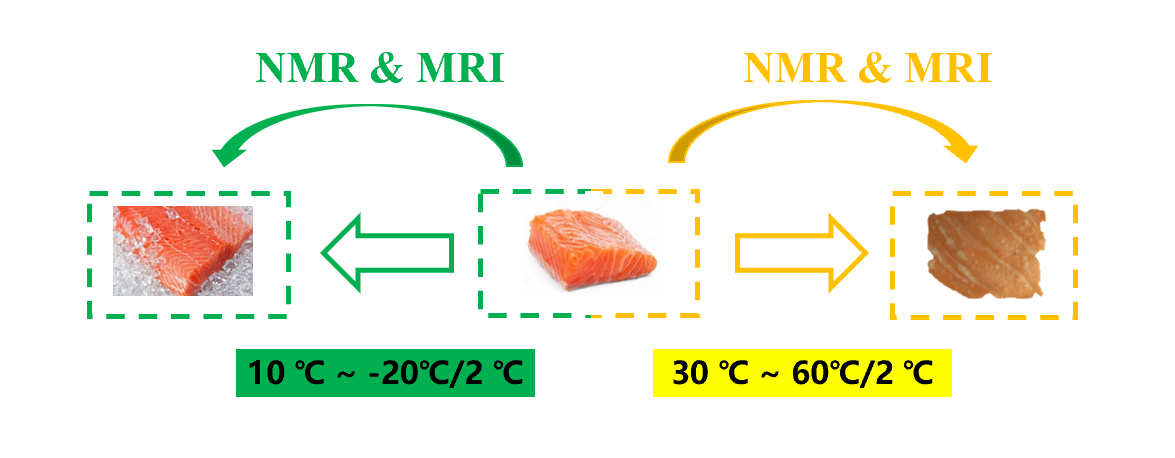
Moisture Migration of Salmon Flesh
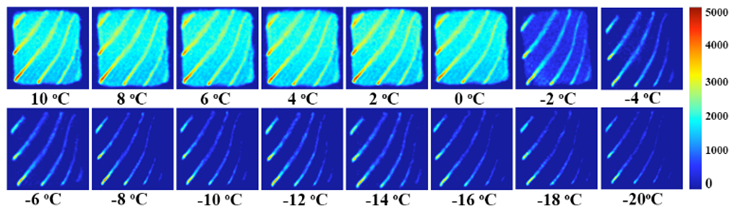
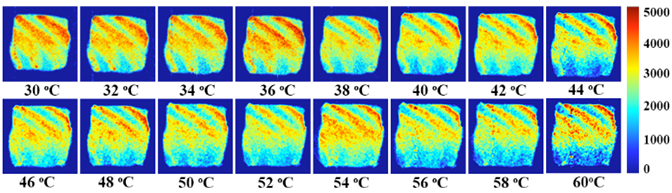
Learning about water migration in salmon protein denaturation and freezing process. First experiment determination of Freezing Point and thermally induced denaturation temperature of salmon flesh. For the determination of freezing point we change the sample temperature from 10℃ to minus 20℃ and testing was done every 2℃ ; For the determination of thermally induced denaturation temperature we change the sample temperature from 30℃ to 60℃ and testing was done every 2℃.
From the MRI images, we can intuitively feel the moisture migration of salmon during the heating and cooling process.
 NIUMAG
NIUMAG