NMR Fat Content Analysis
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectrometer is a powerful analytical technique used to determine the fat content in various substances, including food and biological samples. It does so by taking advantage of the behavior of atomic nuclei in a magnetic field, which provides valuable insights into the molecular structure and composition of a sample.
Principle of NMR: NMR spectroscopy relies on the fact that certain atomic nuclei, such as hydrogen nuclei (protons), exhibit a property called nuclear spin. When placed in a magnetic field, these nuclei align with or against the field. When a radiofrequency pulse is applied, it temporarily disrupts this alignment. When the nuclei return to their equilibrium state, they emit radiofrequency signals that can be detected and analyzed.
Fat Analysis: In the context of fat analysis, the protons in fat molecules are of particular interest. Fat molecules contain long hydrocarbon chains with many protons. These protons have distinct NMR signals that are characteristic of fat.
Data Interpretation: By measuring the NMR signals emitted by protons in the sample, researchers can obtain information about the quantity and chemical environment of fat molecules. The intensity and position of these signals in the NMR spectrum provide valuable data for quantifying fat content and identifying the types of fats present.
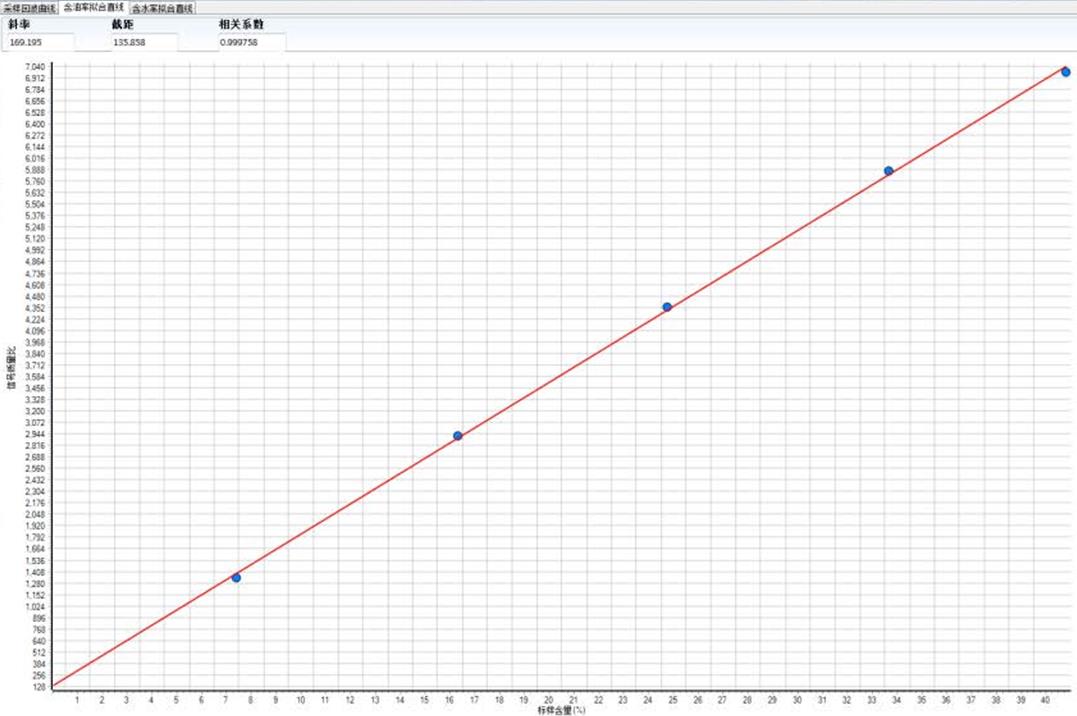
Calibration: To determine fat content accurately, NMR instruments are often calibrated using known standards or reference samples with known fat content. By comparing the NMR signals from the sample to those from the standards, the fat content can be calculated.
NMR Fat Content Calibration
NMR Fat Content in Seeds
NMR (Nuclear Magnetic Resonance) spectrometer can also be employed to determine the fat content in seeds, including various types of edible seeds and oilseeds. Here’s how NMR is applied in assessing fat content in seeds:
Sample Preparation: Seeds need to be prepared appropriately for NMR analysis. This typically involves grinding or homogenizing the seeds to create a representative sample. The sample size and preparation method can vary depending on the specific NMR instrument and technique being used.
NMR Analysis: Quantitative NMR (qNMR): In this method, NMR is used to quantitatively measure the fat content in seeds. The fat molecules in the seeds contain hydrogen nuclei (protons), which produce characteristic NMR signals. By comparing the intensity of these signals to a calibration curve generated from known standards or reference samples, the fat content in the seeds can be determined with high precision.
Data Interpretation: The NMR spectra obtained from the seeds will exhibit peaks or signals corresponding to the protons in the fat molecules. The position and intensity of these peaks are used to calculate the fat content. The chemical environment of these protons can also provide information about the type of fats present, such as saturated or unsaturated fats.
Accuracy and Calibration: To ensure accurate fat content determination, it’s essential to calibrate the NMR instrument using known standards or reference samples with precisely measured fat content. This calibration step is critical for obtaining reliable results.
NMR Fat Content in Seeds Applications
Quality Control: NMR analysis of seeds is valuable for quality control in the agricultural and food industries. It helps ensure that seeds meet the desired fat content specifications for various applications, including oil extraction and food production.
Research and Breeding: NMR analysis can be used in plant breeding programs to select seeds with specific fat content profiles. Researchers can develop seeds with optimal fat content for various agricultural and industrial purposes.
Oilseed Processing: In the oilseed industry, NMR is employed to assess the fat content in seeds before and after oil extraction processes. This information aids in optimizing oil yield and quality.
NMR Fat Content Advantages
Non-Destructive: NMR is a non-destructive technique, allowing for the analysis of seeds without altering or damaging them.
Speed: NMR analysis is relatively fast, making it suitable for routine quality control and research applications.
High Precision: NMR provides highly accurate and precise measurements of fat content in seeds.
 NIUMAG
NIUMAG