En benchtop nmr experiments, there are two main relaxations, spin-lattice relaxation and spin-spin relaxation. The following figure is the recovery curve of T1 and T2.
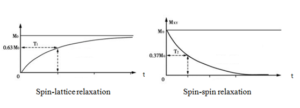
Higo 1: T1 recovery curve and T2 recovery curve
Spin-lattice relaxation is also called longitudinal (or T1) relaxation. t1 is a time that suggests the speed of spin-lattice relaxation. Each material has an instinct resonance frequency. In NMR experiments, if the resonance frequency of material is close to the magnetic frequency, the energy exchange between them will be easy and T1 will be short. If the resonance frequency of material is far from the magnetic frequency, the energy exchange between them will be hard and T1 will be long. En RMN de mesa experiments, the frequency of magnetic field is often less than 23 megahercio; the frequency is very close to the frequency of solid but far from the frequency of liquid. Por lo tanto, solid has a short spin-lattice relaxation time but liquid has a long spin-lattice relaxation time.
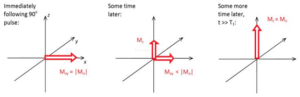
Higo 2: Spin-lattice relaxation abridged general view
Spin-spin relaxation is also called transverse (or T2) relaxation. t2 is a time that suggests the speed of spin-spin relaxation. Each proton can produce a small magnetic field. One proton is influenced by other protons around it. And the influence is determined by the distance between them. Larger is the distance, smaller is the influence. Por lo tanto, t2 is also a instinct character of materials. Protons in solid array are closer than the ones in liquid. So solid has a shorter T2 than liquid. También, we can get another spin-spin relaxation time called T2 *. The only difference between them is that T2 * is not only determined by the distance between the protons but also influenced by the homogeneity of the magnetic field.
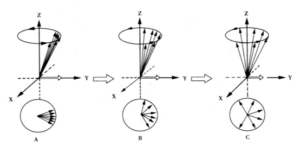
Higo 3: Spin-spin relaxation abridged general view
In specific testing cases, we can analyze the relaxation time to research the relaxation characteristics and other features of the samples.
 mohoso
mohoso
