En el ámbito de la imagen médica, Imagen de resonancia magnética (resonancia magnética) se presenta como una herramienta fundamental, ofreciendo conocimientos incomparables sobre el funcionamiento interno del cuerpo humano. La eficacia de la resonancia magnética., sin embargo, se incrementa significativamente con el uso de agentes de contraste para resonancia magnética (MRI CA). Estos agentes mejoran la visibilidad de las estructuras internas., facilitando así diagnósticos más precisos.
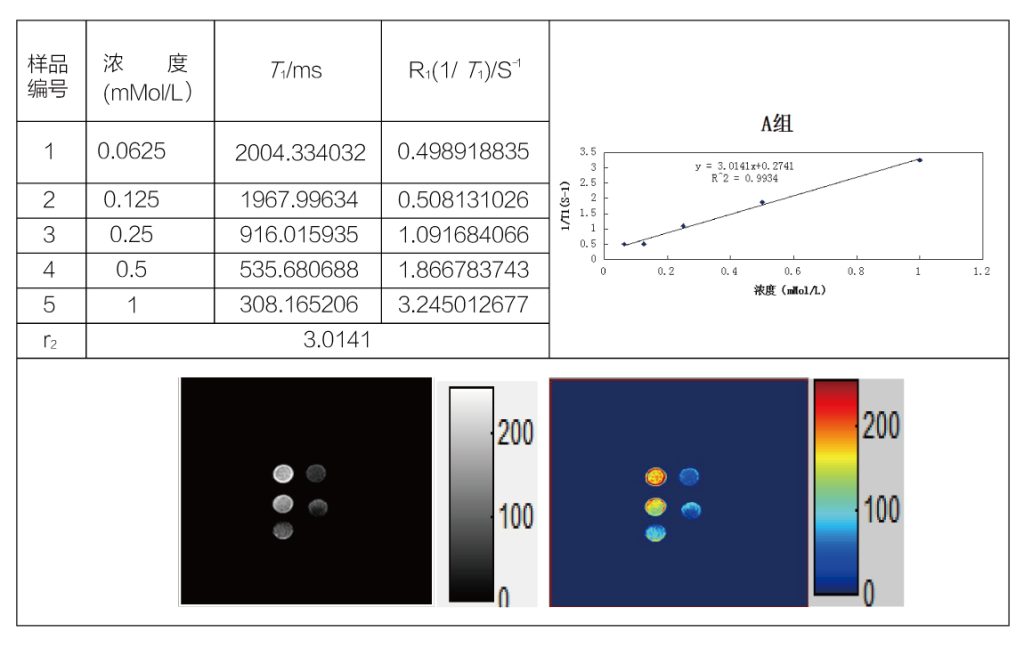
En el centro de la resonancia magnética, su capacidad para influir en los tiempos de relajación de los protones de agua circundantes, una propiedad medida por RMN Relatsometry. Esta técnica, que implica la evaluación de longitudinal (T1) y transversal (T2) Tiempos de relajación, es fundamental para comprender y mejorar el rendimiento de MRI CAS.
La relajación de RMN proporciona una evaluación cuantitativa de la relajación de CAS, Un parámetro que dicta la eficiencia de un agente en el acortamiento de los tiempos de relajación. Con una alta relajación, Incluso una pequeña cantidad de un agente puede producir un efecto de contraste significativo, hacer que el proceso de imagen sea más eficiente y reduciendo la dosis requerida.

Los avances innovadores en la tecnología de RMN han llevado al desarrollo de analizadores de imágenes de RMN compactos, como el NMI20-015V-I, que están específicamente diseñados para el estudio de MRI CAS. Estos dispositivos ofrecen un medio rápido y confiable para probar los tiempos de relajación T1 y T2 e incluso pueden realizar imágenes en muestras de tubos de ensayo, proporcionando datos cualitativos y cuantitativos.
Nuestra exploración en el mundo de MRI CAS a través de la lente de la relajación de RMN ha revelado dos estudios de casos que ejemplifican la aplicación de esta tecnología. El primer caso profundiza en la relajación T1 y el análisis de imágenes ponderadas en T1 de una resonancia magnética, Mostrar la capacidad del agente para alterar la dinámica de relajación de los protones en un entorno controlado.
El segundo estudio de caso presenta un análisis de la relajación de T2 y las imágenes ponderadas en T2, Destacando el profundo impacto de la CA en el proceso de relajación transversal. Estos análisis son cruciales para comprender el comportamiento de MRI CA en diferentes condiciones fisiológicas y para optimizar su formulación para lograr los resultados de imágenes deseados..
El uso de la relajación de RMN no solo acelera el desarrollo de una nueva resonancia magnética, sino que también mejora el refinamiento de los existentes. Proporcionando una comprensión más profunda de los mecanismos de relajación, Esta técnica es fundamental para avanzar en el campo de las imágenes médicas, ofreciendo a los médicos imágenes más claras y, como consecuencia, capacidades de diagnóstico más precisas.
En conclusión, La sinergia entre los agentes de relajación de RMN y el contraste de resonancia magnética es un testimonio del poder de la innovación científica en la atención médica. A medida que continuamos empujando los límites de lo que es posible, El futuro del diagnóstico médico se ve más brillante con cada avance en nuestra capacidad para visualizar las complejidades del cuerpo humano.
 mohoso
mohoso