From the perspective of the technical parameters of NMR, the most commonly used ones include relaxation time (T2 relaxation mostly), nuclear magnetic imaging (MRI) and two-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance.T2 spectrum is probably the most familiar, and NMR imaging technology can clearly show the dynamic changes in the development process, such as the distribution of residual oil in the process of water flooding. Two-dimensional nuclear magnetism doesn’t just take one parameter T2, it takes two parameters T1-T2 or T2-D.
We know that the NMR detects the hydrogen nuclear signal, and if the oil and water are present at the same time, it is very difficult to distinguish the oil and water signal only through the T2 spectrum, so the advantage of two-dimensional nuclear magnetism is shown here. The following figure shows saturated water and saturated light oil collected from the core of a tight reservoir. The vertical axis is T1 time and the horizontal axis is T2 time. It is obvious that the signals of water and oil fall in different zones on the two-dimensional NMR map.
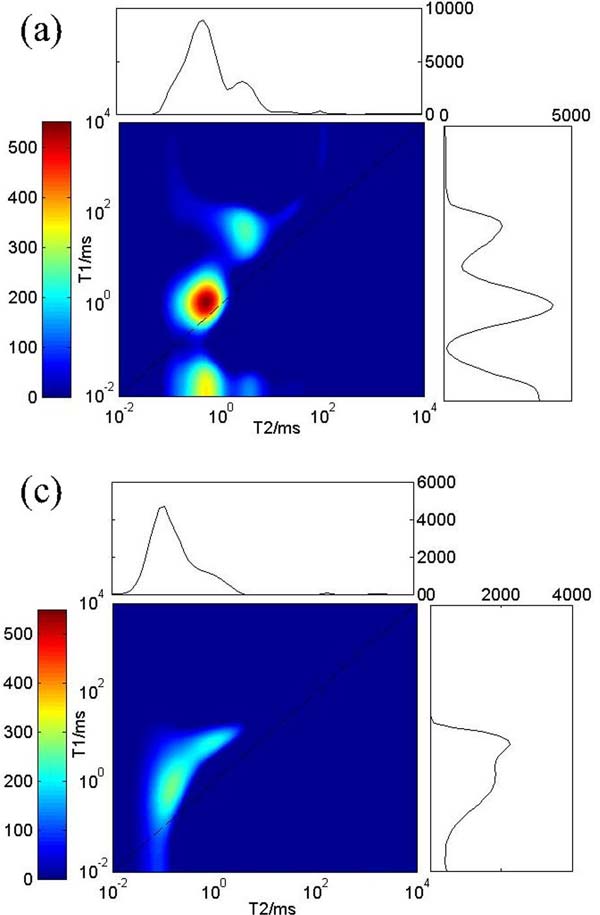
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) can characterize the basic physical parameters of oil and gas reservoirs
Movable fluid saturation and other parameters obtained by NMR Analyzer provide scientific basis for reserve calculation and productivity evaluation.
The most familiar one is probably the calculation of permeability by using nuclear magnetism, which is to calculate the volume of movable fluid and bound fluid through the selection of T2 cutoff value. Currently, Coates model and SDR model are commonly used to calculate nuclear magnetic permeability. Today, a novel example is to use nuclear magnetism to study the fractal dimension of porous media. The fractal dimension D reflects the self-similarity of spatial morphology of porous media. That is to say, if a pore is curved to the naked eye, it should be curved to the microscope. Through mathematical derivation, the fractal dimension formula of nuclear magnetism is obtained.
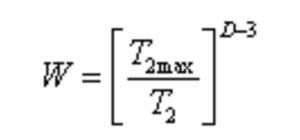
As shown in the figure, after obtaining the NMR fractal dimension of the rock sample, it is divided into the NMR fractal dimension of the large hole and the small hole according to the slope of the two lines, and then the relationship between them and other physical parameters of the sample, such as sorting property, pore volume and so on, is explored respectively, so as to achieve the purpose of reservoir prediction.
Magnetic resonance can be used to study the microscopic mechanism of oil and gas reservoirs
If representational parameters are static, it is dynamic to use nuclear magnetism to study the mechanism of oil, gas and water flow. The ultimate purpose of our study of oil and gas is to guide production, and the process of oil and gas production is a complex multi-field coupling process involving changes in temperature field, pressure field, fluid field, stress field and even chemical field. At present, a series of papers have been published in the international journal SCI on the study of microscopic flow mechanism using nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR).For example, studying the infiltration effect, water lock effect. Nonsteady relative permeability measurement methods and so on were developed. Today, I’m going to list a study of nuclear magnetic resonance in rock mechanics.
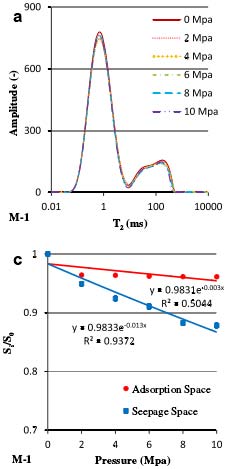
As shown in the figure, nuclear magnetic resonance T2 spectrum is used to calculate the compressibility of coal. Compared with sandstone, coal has the characteristics of high poisson ratio and low young’s modulus. After stress is applied, the pores of coal will be compressed to different degrees. It can be seen from the figure that the seepage hole has a larger shape variable than the adsorption hole.
 NIUMAG
NIUMAG