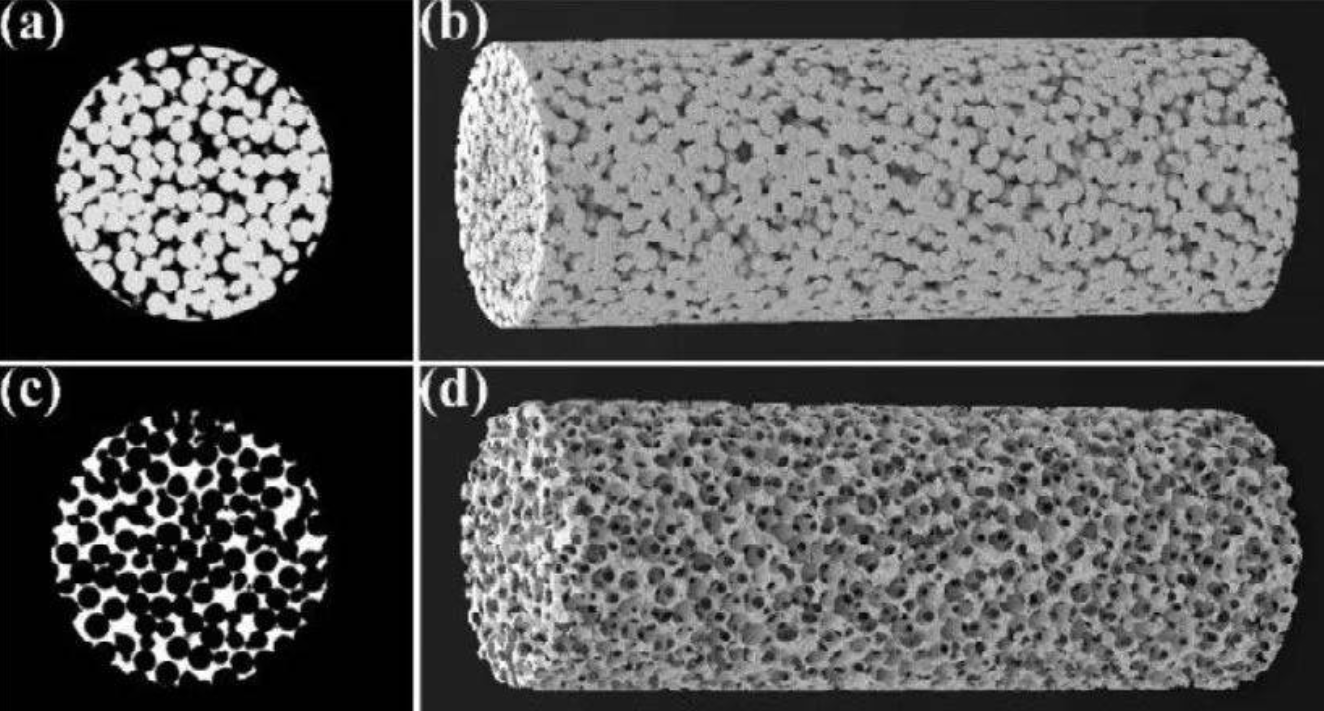
Pore Size Distribution Measured by Low Field NMR
Pore Size Distribution
Pore size distribution refers to the range of sizes of pores within a material or substance. Pores are small voids or spaces within a material that can impact its physical and chemical properties.
The distribution of pore sizes within a material is typically characterized by a pore size distribution curve or histogram, which shows the frequency of pores within different size ranges.
Pore size distribution is important in many fields, including materials science, geology, and biology. For example, in materials science, the pore size distribution of a material can impact its porosity, permeability, and other physical properties. In geology, pore size distribution can impact the movement of fluids through rock formations. In biology, the pore size distribution of cell membranes can impact the transport of molecules in and out of cells.
Pore Size Distribution Measurement Methods
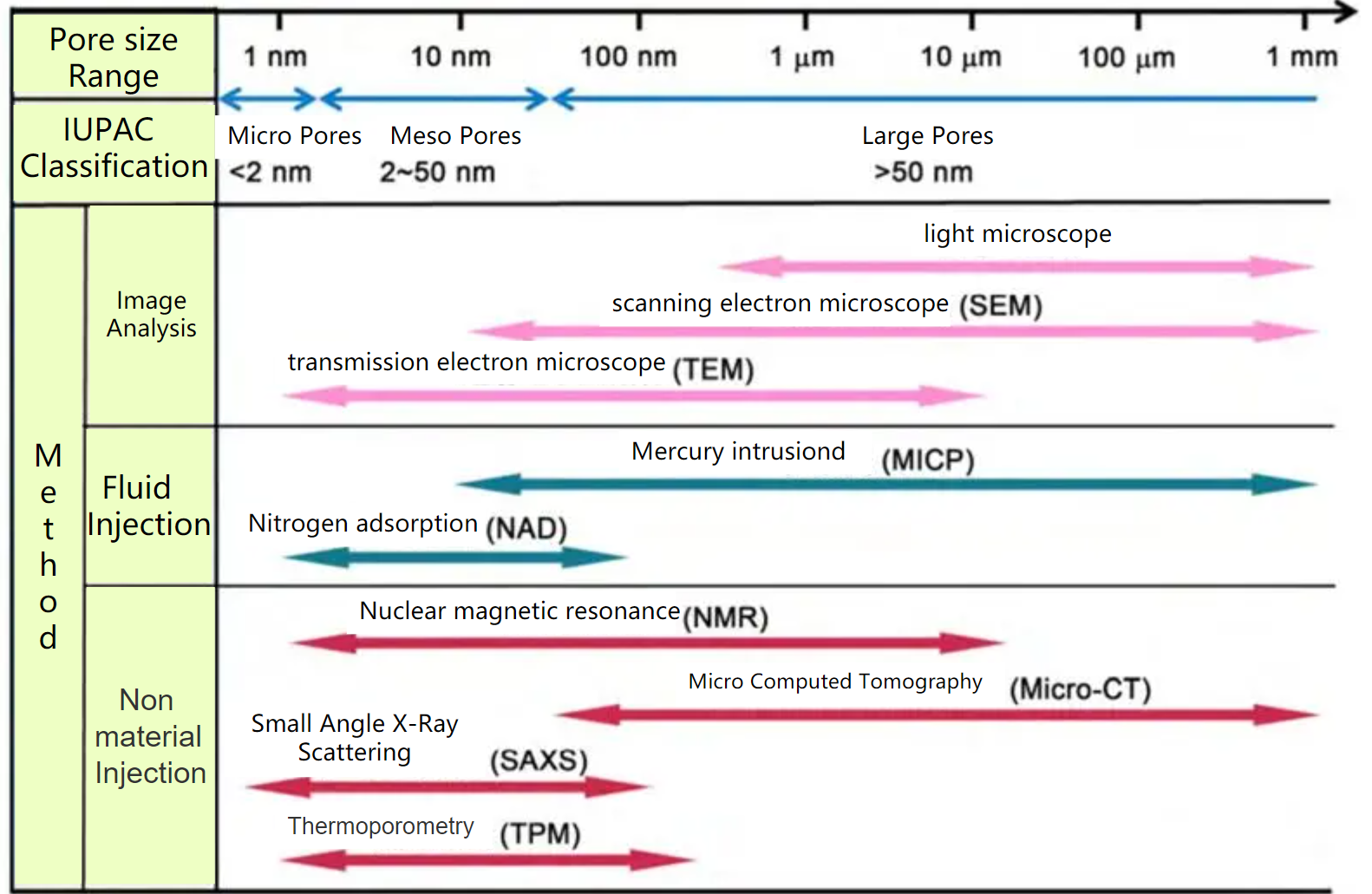
Pore size distribution can be measured using various techniques, such as mercury porosimetry, gas adsorption, and electron microscopy. These methods allow researchers to quantify the pore size distribution of a material and understand how it affects its properties and behavior.
Pore Size Distribution Measured by Low Field NMR
Low field nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) is a technique that can be used to measure the pore size distribution of porous materials.
In this technique, a sample is placed in a magnetic field, and radiofrequency pulses are used to excite the hydrogen nuclei (protons) in the water molecules within the pores of the material. The resulting signals are then detected and analyzed to determine the pore size distribution.
The relaxation times of the hydrogen nuclei are related to the size of the pores in the sample. The T1 relaxation time, for example, is related to the size of the larger pores, while the T2 relaxation time is related to the size of the smaller pores. By measuring both T1 and T2 relaxation times, a complete pore size distribution can be obtained.
Low field NMR has several advantages over other techniques for pore size distribution measurement. It is non-destructive, non-invasive, and can be performed on a wide range of materials, including soils, rocks, and porous media. It also provides information on both the size and connectivity of the pores in the sample.
However, low field NMR has some limitations. It requires a relatively homogeneous magnetic field, and the resolution of the technique may be limited in samples with complex pore structures. Additionally, the interpretation of the data can be complex and requires specialized software and expertise.
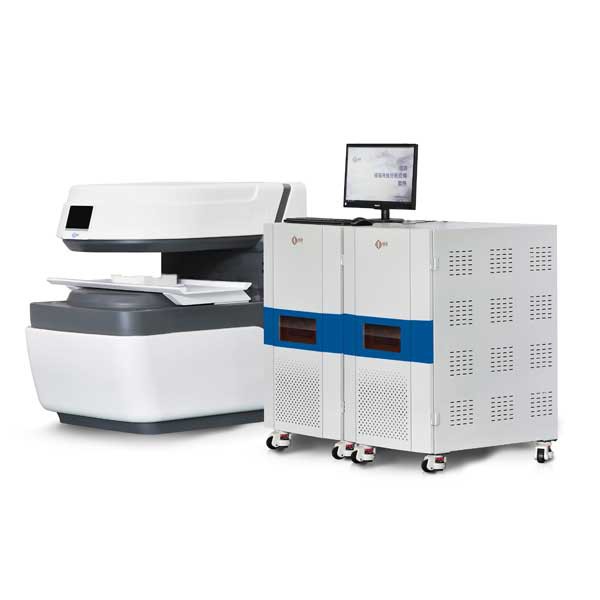
Pore Size Distribution Analysis by Niumag NMR
Niumag provide multiple size NMR instrumentsuse for Pore size distribution measurement, Niumag NMR instruments are capabable with high sensitivity and resolution while maintaining a compact size and affordable cost. These instruments offer a variety of features, including automated shimming, temperature control, and a user-friendly interface for data analysis and processing.
 NIUMAG
NIUMAG