Pore Size Distribution Research
The meaning of pore size distribution
Core pore size distribution refers to the percentage of pore sizes at all layers in the core, it’s calculated by quantity or volume.
The layered pore size distribution refers to the layer stratification of the core in a certain direction, and the calculation of the percentage of the pore size of each layer in terms of quantity or volume.
Significance of layered pore size distribution to reservoir research
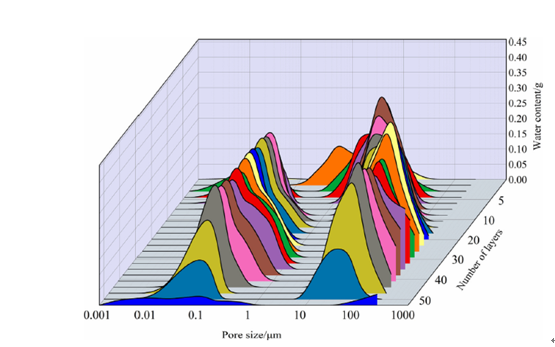
The flow and permeability characteristics of oil and water in oil and gas reservoirs depend on the pore volume space and pore size distribution of the core. Continuously penetrating pore sizes with good fluidity can achieve higher oil recovery. Therefore, the accurate description of layered pore size distribution features are very important to the reservoir. The study of core layered pore size distribution breakthrough the previous study on the spatial pore size distribution.
Research methods of layered pore size distribution
Nowadays, there are many methods for measuring pore size distribution, including mercury intrusion method, liquid nitrogen adsorption method, electron microscope scanning method, X-ray method, etc.
Overview of Measurement Methods for Pore Size Distribution
Mercury intrusion method: it is a method for determining the pore size distribution of some mesopores and macropores. The basic principle is that mercury does not wet general solids, and external pressure needs to be applied to allow mercury to enter the pores. The greater the external pressure, the smaller the radius of the pores that mercury can enter. The pore volume of the corresponding pore size can be known by measuring the amount of mercury entering the pores under different external pressures. However, there is a problem that small pores cannot be measured, and the process is irreversible, which will cause damage to the core, and there may be a problem that the measured value is larger than the actual value.
Liquid nitrogen adsorption method: It is a relatively mature and widely used method to measure the pore size distribution of mesopores by nitrogen adsorption method. It is the principle of volume equivalent substitution, that is, the amount of liquid nitrogen filled in the hole is equivalent to the volume of the hole. There is a bias in the test of macropores based on the principle of liquid nitrogen adsorption.
Electron microscope scanning method: slice the core, expose it under the electron microscope, photograph the cut surface with high resolution, set the threshold value to select the shadow area to define the pore, and obtain the pore size distribution after data processing of the photo. This method requires slicing the core, the process is irreversible and destroys the sample, and the threshold setting is subjective, which has a certain impact on the accuracy of the pore size distribution.
X-ray method: X-rays pass through the core and exhibit exponential attenuation. When the receiver receives the attenuated signal, after data processing, a correlation can be established between the amount of the attenuated signal and the sample pores, so as to obtain the pore size distribution of the core. . However, the size of the core penetrated by X-rays has a certain limit, and different minerals in the core will affect the attenuation of X-rays, thereby affecting the testing accuracy of the aperture.
Compared with traditional methods, NMR, as a mature pore size distribution research method, NMR has the advantages of fast, non-destructive, online monitoring, accurate, green, etc. It can realize spatial layer of cores, test the pore size distribution of each layer, and more microscopically characterize the pore size distribution.
Research and application of low-field NMR in pore size distribution
The spontaneous imbibition process of the core was studied by the characterization technique of layered pore size distribution brought by low-field NMR. The results show that the imbibition rate of the sample when the imbibition direction is parallel to the bedding is greater than that when it is perpendicular to the base. After the core self-absorbs water, the degree of right shift of the NMR T2 spectrum is low, indicating that the core’s ability to absorb water to generate micro-fractures is weak, and the water in the small pores does not flow to the large pores, that is, water lock is likely to occur. It is recommended to prevent the reservoir during the development process. Damage is the main thing. The spontaneous imbibition characteristics of reservoir samples and their influencing factors are revealed, which has important guiding significance for enhancing oil recovery.
 NIUMAG
NIUMAG