Sistema de resonancia magnética para animales pequeños en la evaluación de lesiones cerebrales en ratas
Small Animal MRI is a powerful non-invasive tool that can be used to detect a wide variety of lesions.
Niumag ha desarrollado y producido un nuevo compacto, Sistema de resonancia magnética para animales pequeños de alto rendimiento que utiliza un diseño de RMN de campo bajo. Este sistema de resonancia magnética para animales pequeños es un enfoque basado en aplicaciones, Reducir el coste y la complejidad de los sistemas tradicionales.. El sistema de resonancia magnética para animales pequeños es móvil y está autoprotegido y puede colocarse en la mayoría de las instalaciones de investigación.. No refrigerant or utility supply is required of this small animal MRI. The advantage of this small animal MRI system is that it can easily provide clear 3D digital morphological images of the entire target organ.
In small animal MRI analysis, spin-lattice relaxation time (T1) and spin-spin relaxation time (T2) values are frequently encountered, the normal patterns of which vary by organ, tissue, and fluid . When brain injury was induced in rats, T1 and T2 signals were correspondingly altered due to tissue changes; these T1 and T2-weighted image changes allowed us to detect induced brain injury.
Pilocarpine, a muscarinic cholinergic agonist, is a widely accepted drug for inducing epilepsy and morphological neuronal damage in the rat brain. In this neuronal injury model, clear histological brain injury can be observed in multiple parts of the brain, such as the piriform cortex, lateral dorsal nucleus of the thalamus, hippocampus, and substantia nigra.
Small Animal MRI Analysis
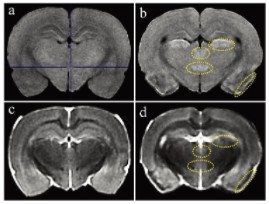
Cifra 1 shows T1 and T2 weighted MRI images. Compared with controls, pilocarpine-treated animals showed high T1 signal in the piriform cortex, lateral thalamic nucleus, retroperiventricular nucleus of the thalamus, and posterior hypothalamic nucleus of the brain (Figure 1a and b). In T2-weighted images of pilocarpine-treated animals, compared with controls, low T2 signal was observed in the piriform cortex, corresponding to areas of high T1 signal (Figure 1c and d). The T2 signal intensities of the other 3 areas of high T1 signal were comparable to those in the control group (moderate intensity) (Figures 1c and d).
Applicability of an easy-to-use compact small animal MRI system in the clinical toxicology-pathological examination of pilocarpine-induced rat brain injury. High T1 and low T2 signals showed marked histopathological neuronal damage, although histopathological examination was more sensitive.
The use of small animal MRI systems produced by Niumag is of high value for the study of brain injury.
 mohoso
mohoso