Solid Fat Content NMR
Solid Fat Content Background
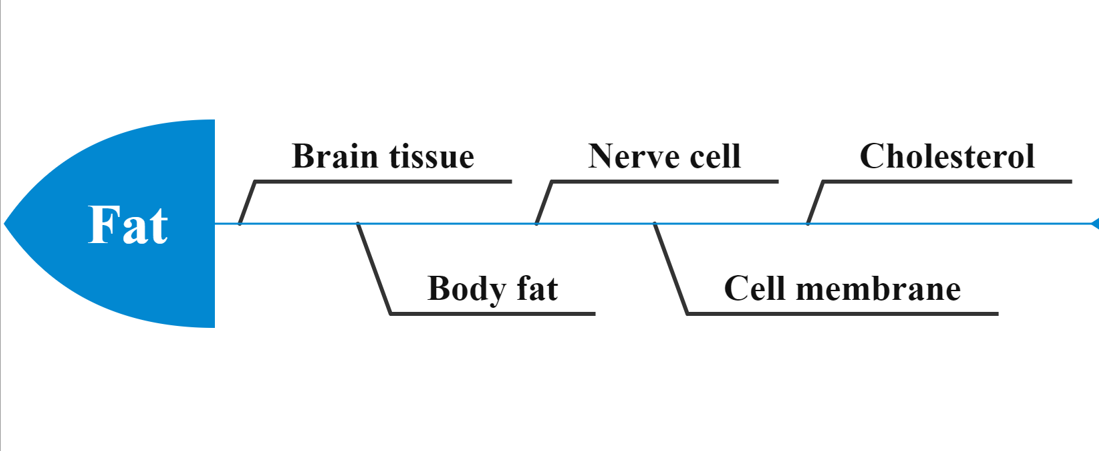
Fat is essential to us and is the cell membrane. Important building blocks of neurons, brain tissue, cholesterol, and body fat.
There are many kinds of oils and fats. Common edible oils and fats are divided into 5 categories. Dairy fats – from ruminant milk, vegetable fats – similar to palm oil, olive oil, cocoa, can be used to produce candy, chocolate, animal fats – from In livestock fats, marine animal and algae oils – derived from fish oil, cod liver oil and algae oils, lauric acid has been commonly found in fruit seeds.
The melting point of oil affects the digestion and absorption rate of the human body. 1. The melting point is lower than 37°C. Because it is easy to emulsify, the digestion and absorption rate is 97~98%. 2. The melting point is 40~50℃, and the digestion and absorption rate is 90%. 3. The melting point is higher than 50°C, which is difficult to absorb and digest.
Solid fat content
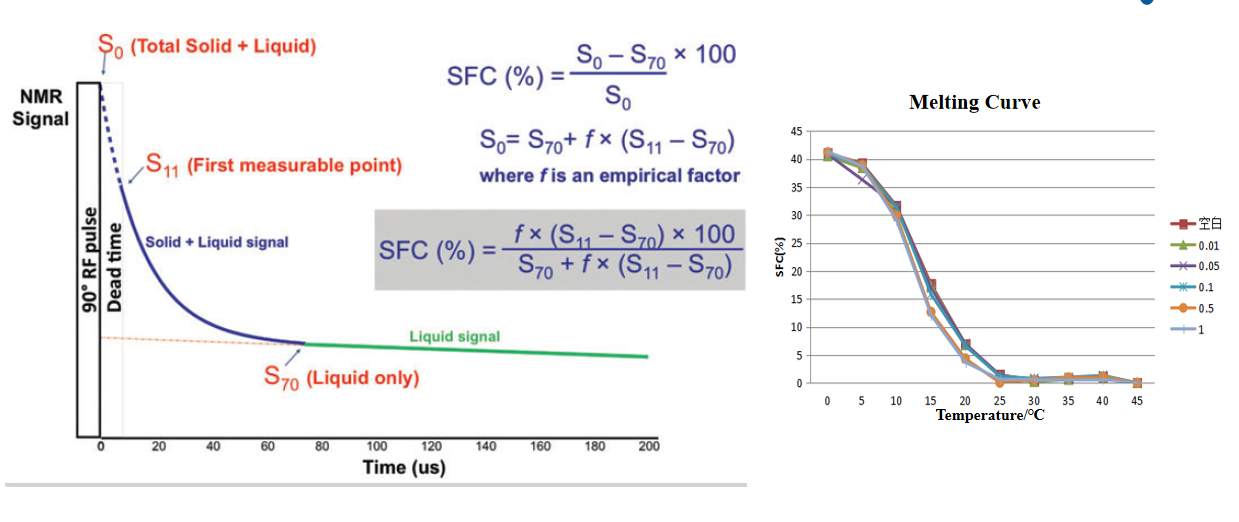
Solid fat content SFC is the percentage of the number of protons in the solid phase to the total number of protons in the solid-liquid phase at a specified temperature.
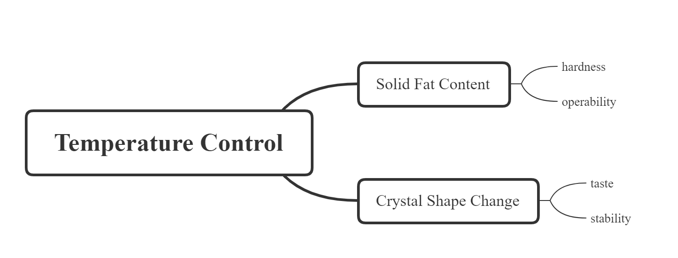
In oil production, it is often required that the solid precipitated has certain physical properties to meet the needs of various applications, which requires the formation of crystals and the conversion of different crystal types to be controlled well.
Solid Fat Content Test
Traditional method: melting expansion or DSC
- Using empirical formula
- Long test time
- Poor test repeatability
- Complex operation process
- Result is about 10% lower when the content is higher
NMR method:
- According to the different NMR properties of the solid and liquid phases
- Test time less than 16s
- Good repeatability
- Simple operation process
- Measure oil and water simultaneously
Solid Fat Content NMR Signal
Solid Fat Content NMR Analyzer
 NIUMAG
NIUMAG


WeChat
Scan the QR Code with WeChat