Natural gas hydrate refers to the crystal compound, commonly known as “combustible ice”, in which methane molecules are enclosed in the crystal lattice of water molecules at low temperature and high pressure. China is rich in natural gas hydrate resources. In practice, however, the process is fraught with difficulties.
Different from conventional natural gas reservoirs, hydrate reservoirs have complex and diverse mineral compositions. The sediments are mainly argillaceous siltstones, and the pores are mainly developed with small pores and extremely low permeability. And the formation conditions are extremely harsh, such as: need low temperature (generally below 10℃) high pressure (several MPa above) deep pyrolysis gas and shallow microbial origin of biological gas, favorable storage space.
The study on the formation of gas hydrate in sandstone can provide strong research support for practical exploitation.
Apparatus
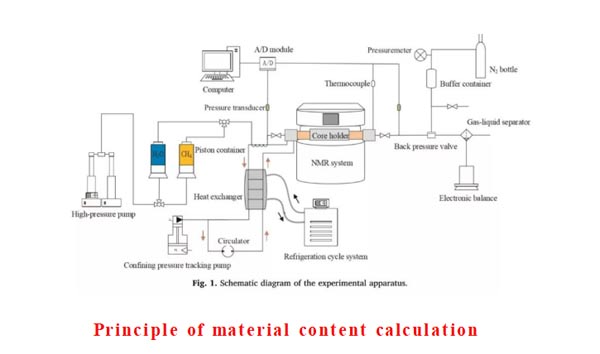
- Calculation of methane production:
The excess gas method is selected to ensure sufficient supply of methane gas during the formation of hydrate, so the reduction of liquid water corresponds to the production of solid hydrate. Methane saturation can be calculated according to the formula.
2.Accuracy of NMR Spectrum:
The confining pressure and pore pressure are kept constant and constant (such as 4MPa), so the effect of stress on pore structure is eliminated. In this way, the spectrum changes of water detected by nuclear magnetic field are all caused by the formation of hydrate
3.Continuity monitoring of the process:
The synthesis and decomposition process of hydrate can be observed continuously and dynamically by alternating T2 NMR and MRI scanning.
 NIUMAG
NIUMAG