Dispersion of particles in a liquid medium is crucial for various industrial and scientific applications. Low field nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) technology has emerged as a non-invasive and rapid method to evaluate the dispersibility of particle suspensions. This article delves into the principles and advantages of using low field NMR for assessing particle dispersibility.
Particle dispersibility refers to the process where particles in a liquid medium separate and distribute evenly throughout the medium. Dispersing particles effectively is essential for optimizing product performance and consistency. Low field NMR offers a unique approach to understanding and enhancing the dispersibility of particles in suspensions.
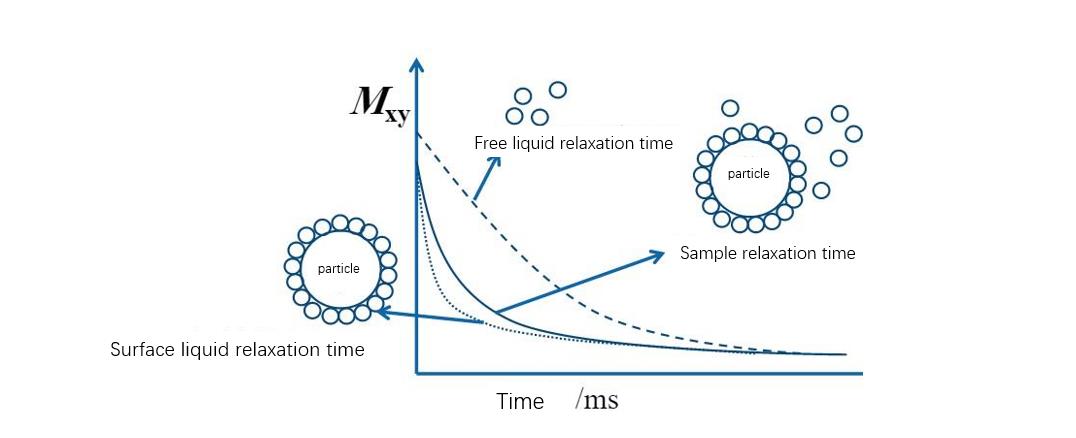
Mechanical stirring and the use of organic solvents are traditional methods for particle dispersion. However, these techniques have limitations, such as introducing impurities or restricting the formation of ultrafine particles. Low field NMR, on the other hand, provides a non-destructive and repeatable measurement, minimizing the amount of sample material needed for stability studies.
The principle behind low field NMR in evaluating dispersibility is the correlation between solvent relaxation rates and the available particle surface area. In a well-dispersed system, solvent molecules near the particle surface exhibit increased relaxation rates due to altered mobility. This change is detectable by low field NMR, allowing for the quantitative assessment of particle dispersion.

Advantages of Low Field NMR:
1. Non-Invasive Measurement: The measurement can be performed repeatedly on the same sample, reducing material consumption and sample variability.
2. Applicability in Research and Industry: Low field NMR is suitable for both scientific research and industrial applications, providing a versatile tool for particle dispersion analysis.
3. Direct Observation of Dispersion Effects: Unlike other methods that require sample preparation or destruction, low field NMR allows for direct observation of dispersion effects on the sample.
Low field NMR is a powerful tool for evaluating the dispersibility of particle suspensions. Its non-invasive nature, coupled with the ability to perform repeated measurements on the same sample, makes it an ideal choice for stability studies and quality control in various industries. By understanding the principles of particle dispersion and leveraging the capabilities of low field NMR, scientists and engineers can optimize particle suspensions for enhanced performance and consistency.
Keywords: Low field NMR, particle dispersibility, non-invasive measurement, particle suspension evaluation, industrial applications, scientific research, stability studies, particle surface area, solvent relaxation rates.
 NIUMAG
NIUMAG