In the intricate realm of medical imaging, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) stands as a cornerstone, offering non-invasive insights into the body’s internal structures with unparalleled soft tissue contrast. A pivotal aspect of MRI’s diagnostic prowess lies in the use of contrast agents, which selectively enhance the visibility of specific tissues or pathologies. These agents, categorized into three primary types – paramagnetic positive contrast agents, susceptibility negative contrast agents, and superparamagnetic iron oxide particles – each bring unique capabilities to the imaging table. This article delves into the application of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) relaxometry analysis in understanding and optimizing these essential MRI contrast agents.
Introduction to NMR Relaxometry in MRI Context
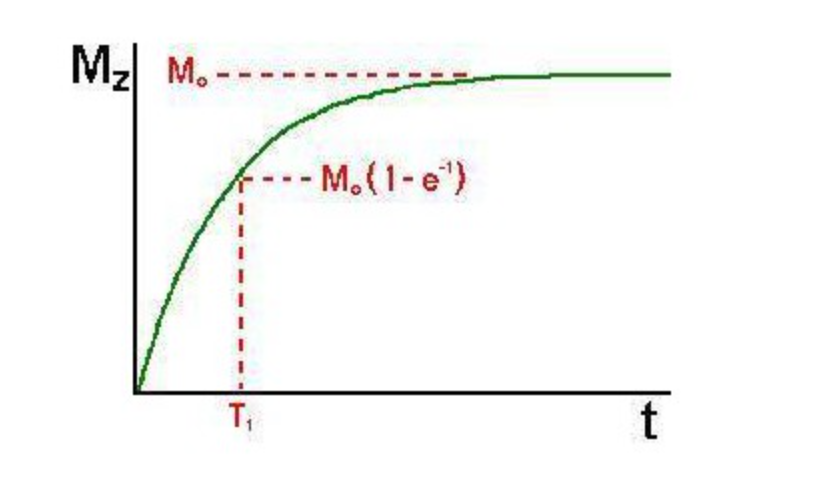
NMR relaxometry, a subset of NMR Analyzer, focuses on quantifying the relaxation times (T1 and T2) that govern the signal intensity in MRI scans. T1 relaxation, or longitudinal relaxation, refers to the time required for excited nuclei to return to their equilibrium state. Conversely, T2 relaxation, or transverse relaxation, measures the decay of coherence between nuclei in the transverse plane. By precisely measuring these parameters, NMR relaxometry provides crucial information about the molecular environment within a sample, including the presence and characteristics of contrast agents.
Paramagnetic Positive Contrast Agents: Boosting Signal Intensity

Paramagnetic contrast agents, such as gadolinium-based compounds, exhibit strong magnetic moments due to unpaired electrons. They shorten both T1 and T2 relaxation times, resulting in brighter images (T1-weighted) where they accumulate. NMR relaxometry plays a pivotal role in characterizing these agents by directly measuring their impact on relaxation rates (R1 and R2). The MiniPQ001-20-015V, a specialized NMR relaxometry instrument, can quantify the T1, T2, R1, and R2 values of different concentrations of gadolinium-based contrast agents, thereby assisting researchers in fine-tuning formulations for optimal imaging efficacy.
Susceptibility Negative Contrast Agents: Enhancing Contrast through Darkening
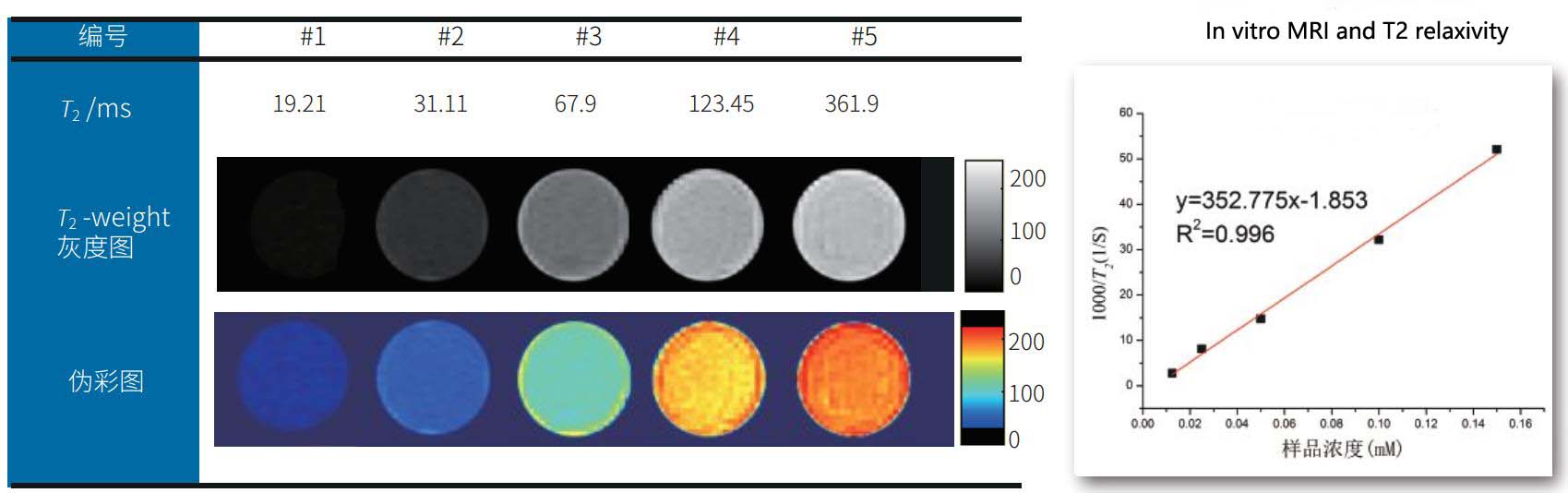
Susceptibility negative contrast agents, like iron oxide nanoparticles, exploit local magnetic field inhomogeneities to create areas of signal void or decreased signal intensity in T2- and T2*-weighted images. This effect is particularly useful for visualizing vessels or cystic structures. NMR relaxometry aids in understanding the complex interaction between these particles and the surrounding tissue, allowing for optimization of particle size, concentration, and stability to minimize unwanted side effects while maximizing contrast efficiency.
Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Particles: Tunable Relaxation Properties
Superparamagnetic iron oxide (SPIO) particles represent a subset of susceptibility agents with unique properties. They exhibit superparamagnetism at physiological temperatures, enabling rapid alignment with an external magnetic field and rapid relaxation upon its removal. SPIOs can be tailored to either enhance or decrease signal intensity, depending on the imaging sequence. NMR relaxometry is instrumental in deciphering the intricate interplay between particle aggregation, dispersion, and the surrounding microenvironment, ensuring precise control over their relaxation behavior.
Advancements and Applications
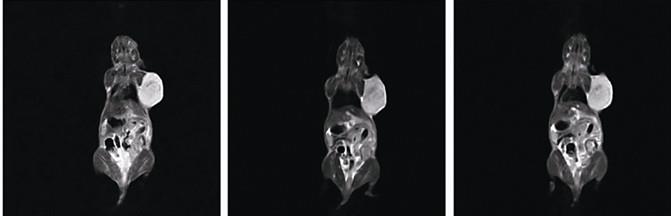
The development of novel contrast agents demands rigorous characterization to ensure safety and efficacy. NMR relaxometry instruments, with their ability to directly test and quantify relaxation parameters, have become indispensable tools in this pursuit. They facilitate the optimization of agent design, enabling targeted delivery systems, and enhancing the specificity of contrast enhancement. In addition, the evaluation of these agents under various physiological conditions simulates real-world applications, ensuring their performance matches clinical expectations.
The Future of MRI Contrast Agent Optimization
In the quest for advanced medical imaging, NMR relaxometry emerges as a linchpin technology in the design, testing, and optimization of MRI contrast agents. By providing a detailed understanding of relaxation dynamics, it paves the way for the creation of next-generation contrast materials that are safer, more efficient, and tailored to specific diagnostic needs. As research in this field progresses, we can anticipate an era where MRI contrast agents are not only capable of detecting but also monitoring therapeutic responses, thus revolutionizing personalized medicine. The integration of cutting-edge NMR relaxometry techniques ensures that this vision becomes a reality, fostering advancements that align with the evolving landscape of healthcare and the pursuit of improved patient outcomes.
 NIUMAG
NIUMAG