Distribución de agua en los alimentos
NMR analysis of water has an important theoretical basis, which is the joint induction theory proposed by Ling in 1962: the inherent charge of the macromolecule and the opposite charge connected to it force a large amount of water to form a polar multilayer model. Debido a la restricción de las moléculas de agua., la diferencia en la velocidad de atenuación se muestra en el espectro de RMN. Cuanto mayor sea la moderación, cuanto menor sea el tiempo de relajación. Generalmente, El agua se puede dividir en tres tipos.: agua gratis, agua inmóvil y agua ligada.
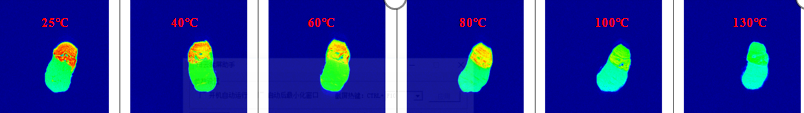
Water Distribution of Drying of Pork at Different Temperatures
Pork drying at different temperatures – oil and water distribution – migración de agua – cross section water distribution
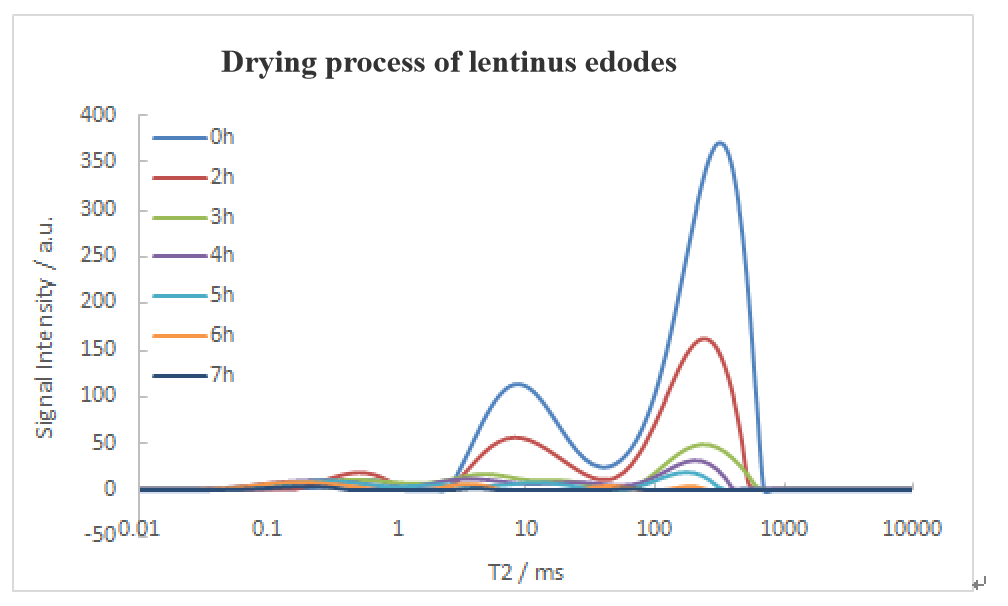
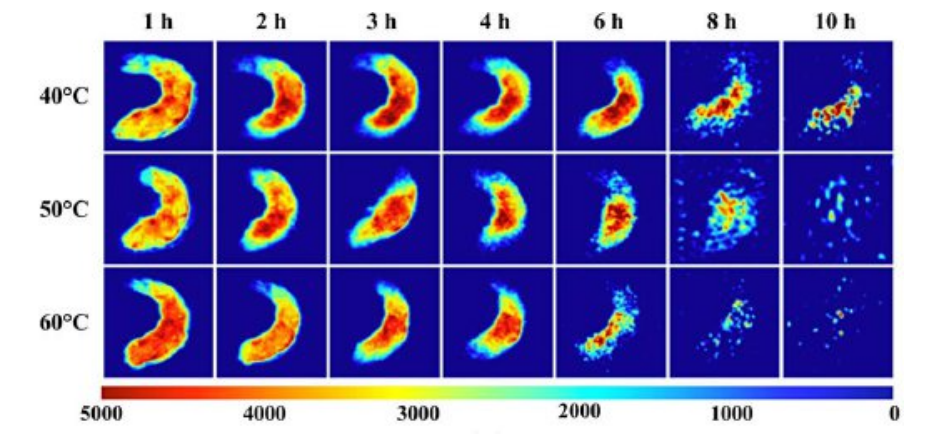
Water Distribution MRI of Lentinula Edodes Under Different Drying Conditions
En el espectro de relajación, the greater the peak time, the greater the corresponding water activity. The larger the peak signal intensity or area, the more water content corresponds to the water state
With the increase of drying time, the peak intensity of T22 and T23 gradually decreased, eso es, the content of non-flowing water and free water gradually decreased. The peak position gradually moved to the left, eso es, the water activity gradually decreased.
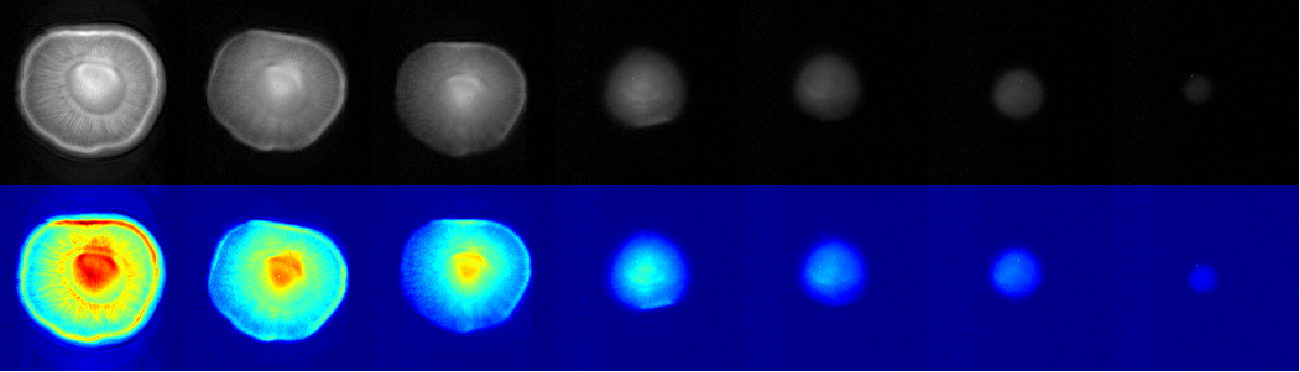
Water Distribution Change during Shrimp Dehydration
With the extension of the drying time, the size of the brighter area continues to decrease, indicating that the signal of the long relaxation water is lost during the dehydration process.
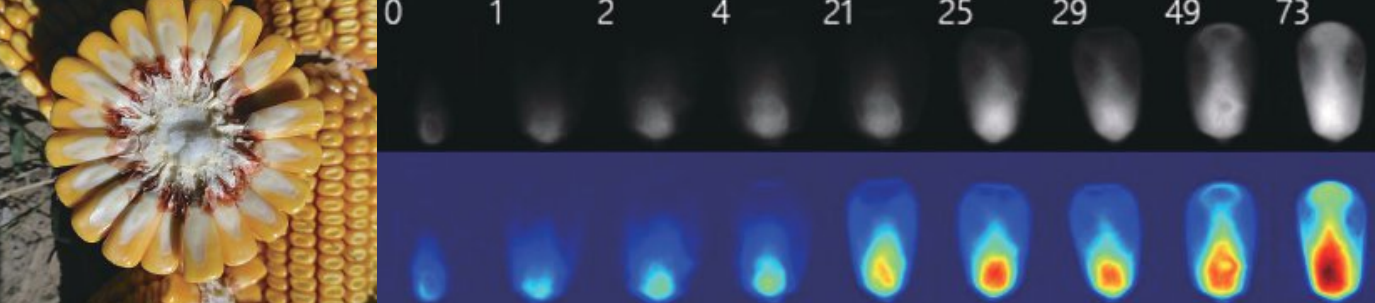
Water Distribution Change of Single-family Corn During Soaking
Water Distribution MRI of Fruit and Vegetables
 mohoso
mohoso