Investigación sobre la distribución de agua en la carne de yak
After the slaughter of livestock, fresh meat still maintains the cell structure. The structure of the muscle tissue and the processing method of the fresh meat will affect the water distribution in the meat, and affect the water retention of the fresh meat in the end. Por lo tanto, the moisture change of fresh meat in the process of ripening and fresh-keeping storage has been widely concerned.
For water distribution analysis, RMN de campo bajo (lowfield NMR, RMN-LF) is a fast, non-destructive analysis and detection technology. It can determine the different states of moisture in meat by measuring the relaxation characteristics of hydrogen nuclei in meat. Many studies on NMR methods in the field of meat products have worked out, mainly focusing on the following three aspects:
1) Water distribution and water migration in different states research in meat and meat products;
2) Judging the eating quality and processing quality of meat combining with other indicators;
3) Carry out meat identification for water injection and glue injection, identification of heterogeneous meat and detection of meat freshness.
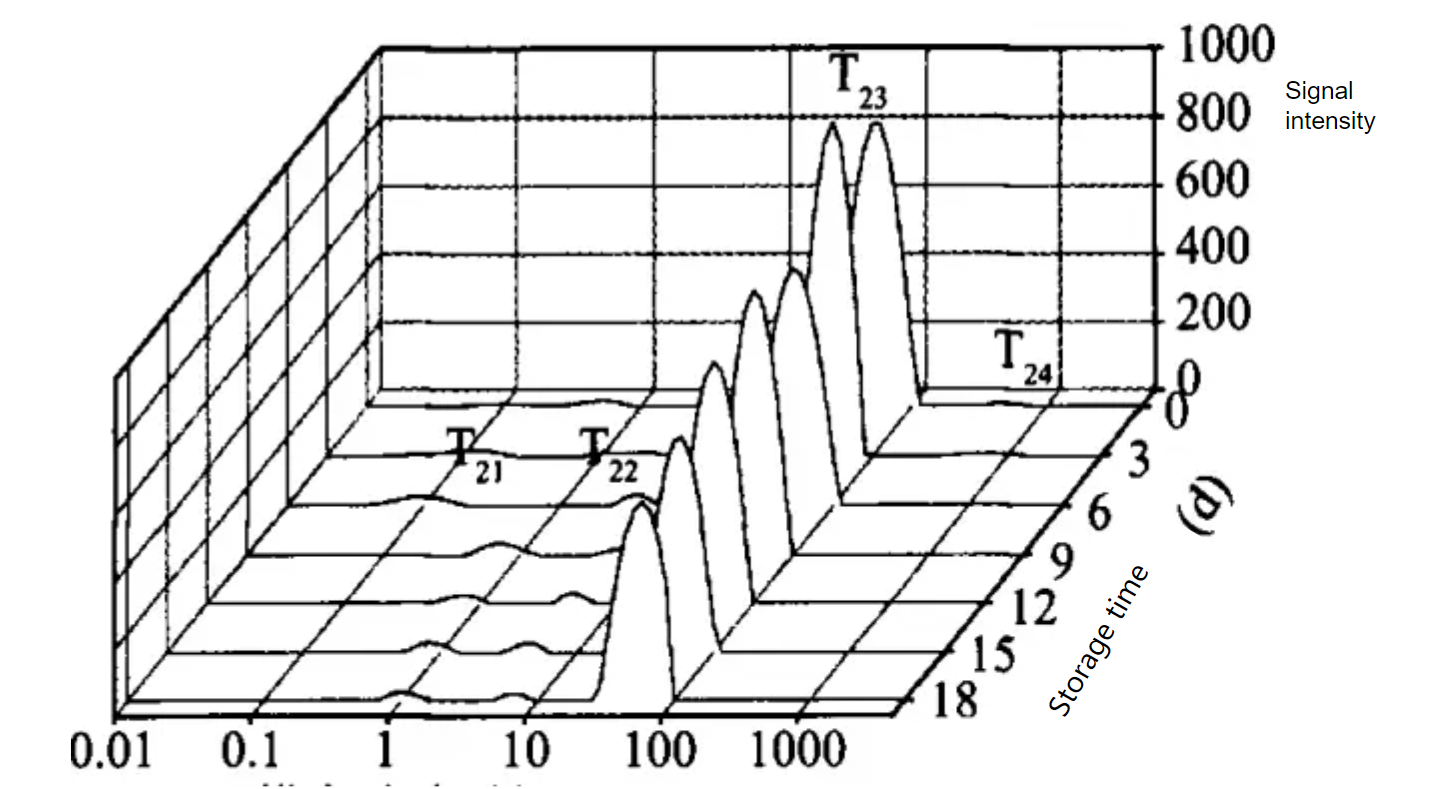
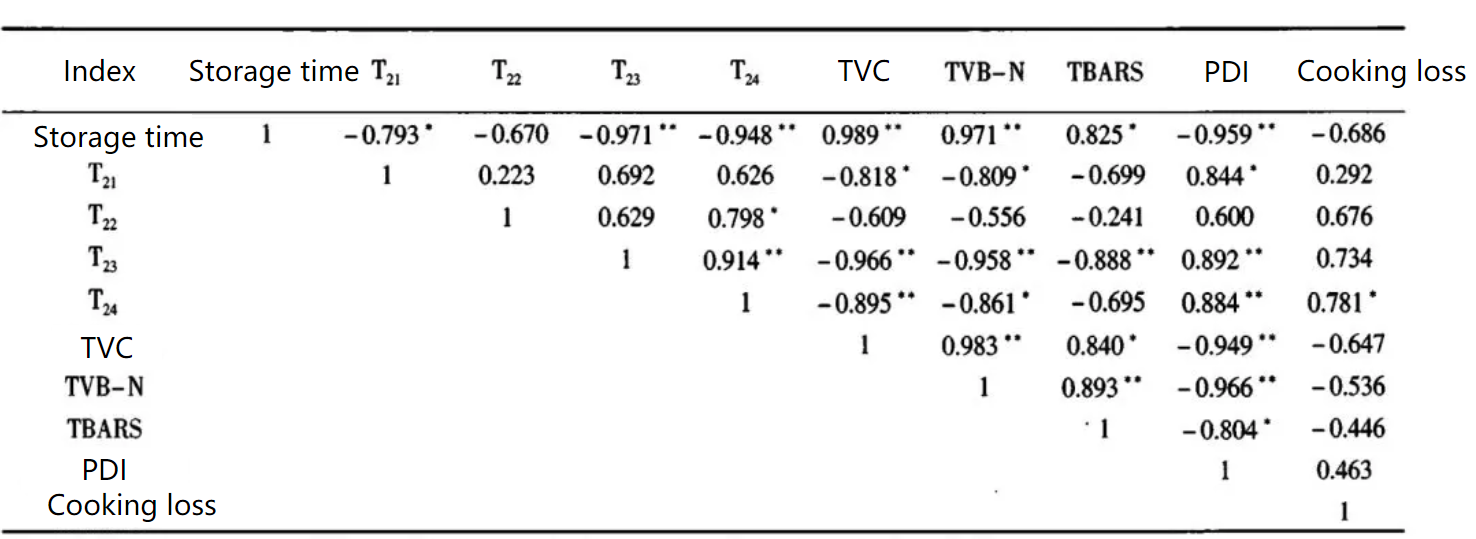
Literature conclusions: The non-flowing water and free water in meat are related to the water holding capacity, water retention, flavor and other quality indicators of meat. From the correlation analysis, we can see that during the storage of yak meat, the changes of physical and chemical properties are often accompanied by the changes of the mobility of water molecules in the meat. We can use T2 relaxation time cto evaluate the quality of yak meat after different storage times.
Transverse relaxation time distribution of yak meat during storage
Correlation Analysis of Yak Meat Indexes
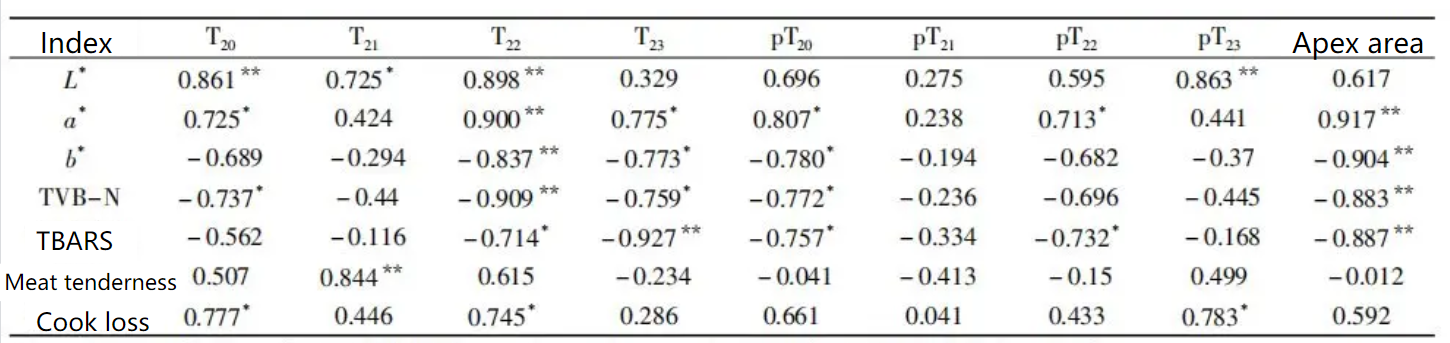
Literature conclusion: By correlation analysis of yak meat quality index and NMR parameter T2, it is found that T22 has a strong correlation with each quality parameter, so the change of beef quality can be characterized according to the change of T22.
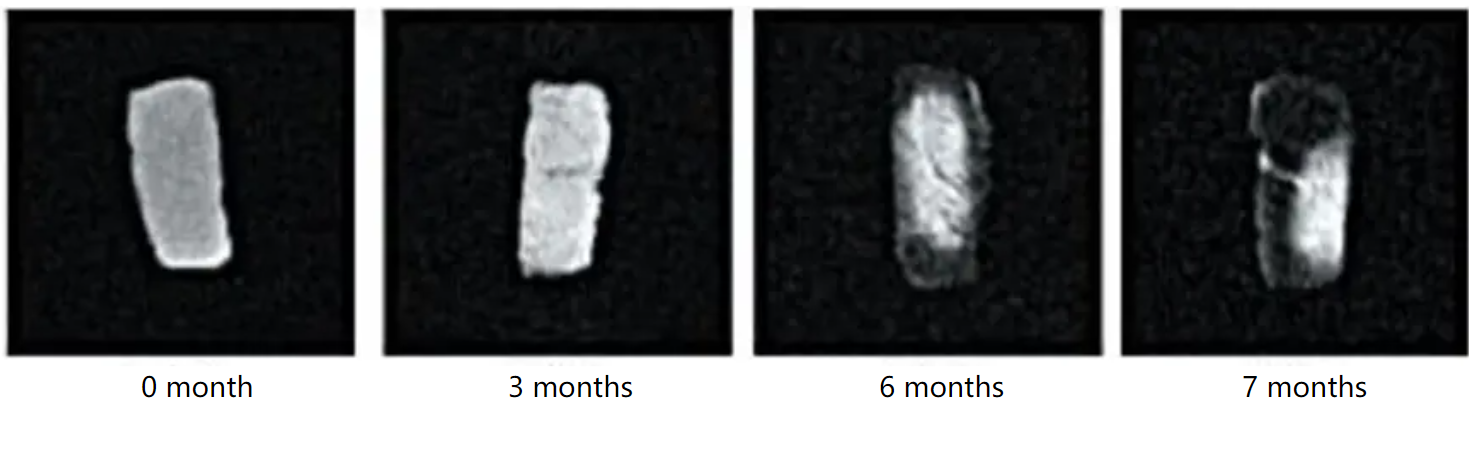
Por experimentos de resonancia magnética, podemos ver que el consumo seco de carne de yak almacenada a -10°C era grave, y la retención de agua de la carne era débil, que no era propicio para el almacenamiento a largo plazo de carne de yak. Considerando la pérdida de agua y el costo económico, La carne de yak debe almacenarse por debajo de Tg en la medida de lo posible., and it is advisable to control it at about -15–20°C.
Correlation coefficient between LF-NMR T2 and measurement index
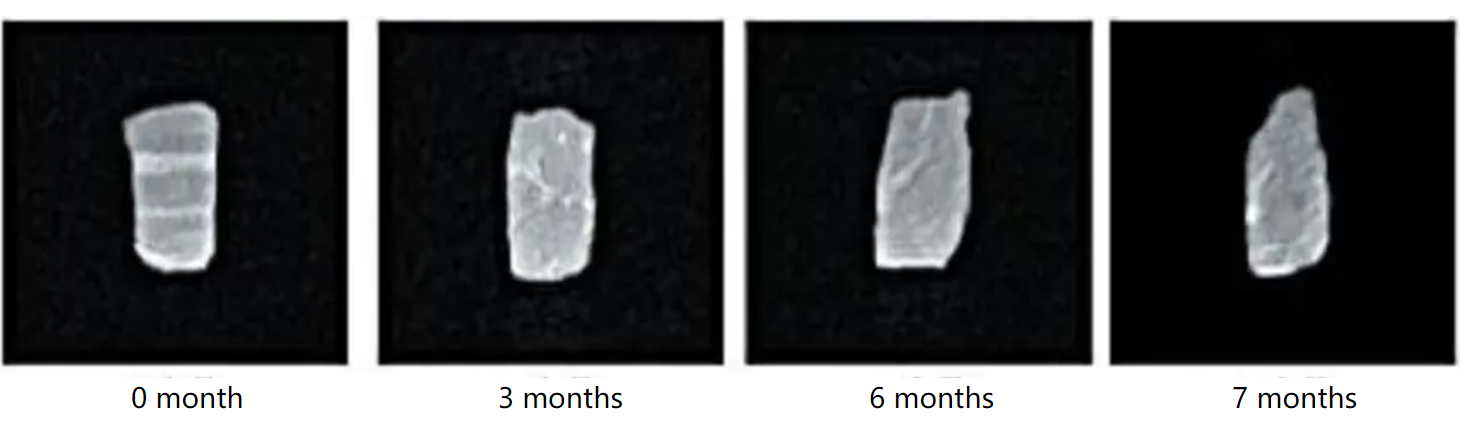
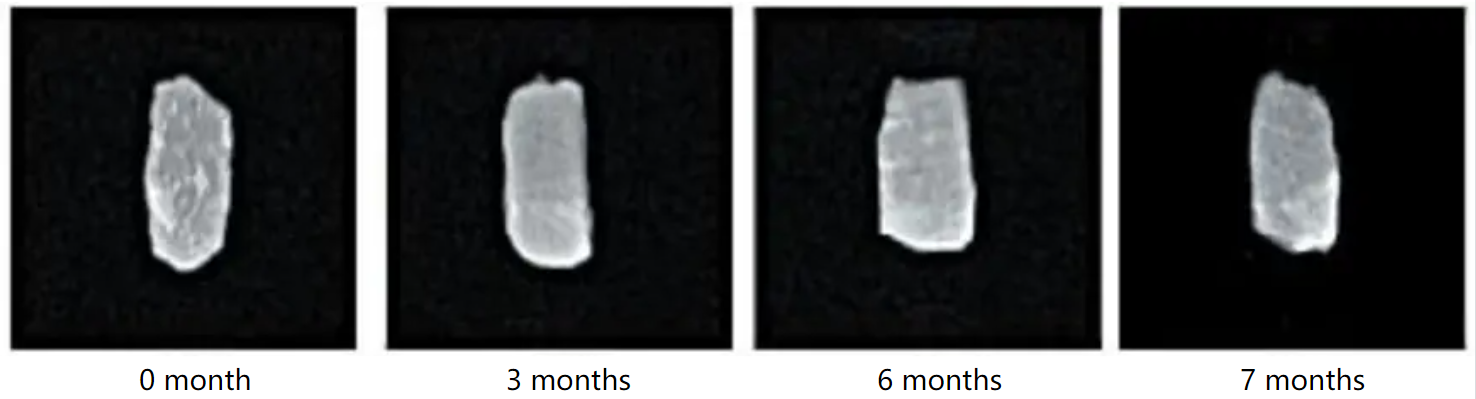
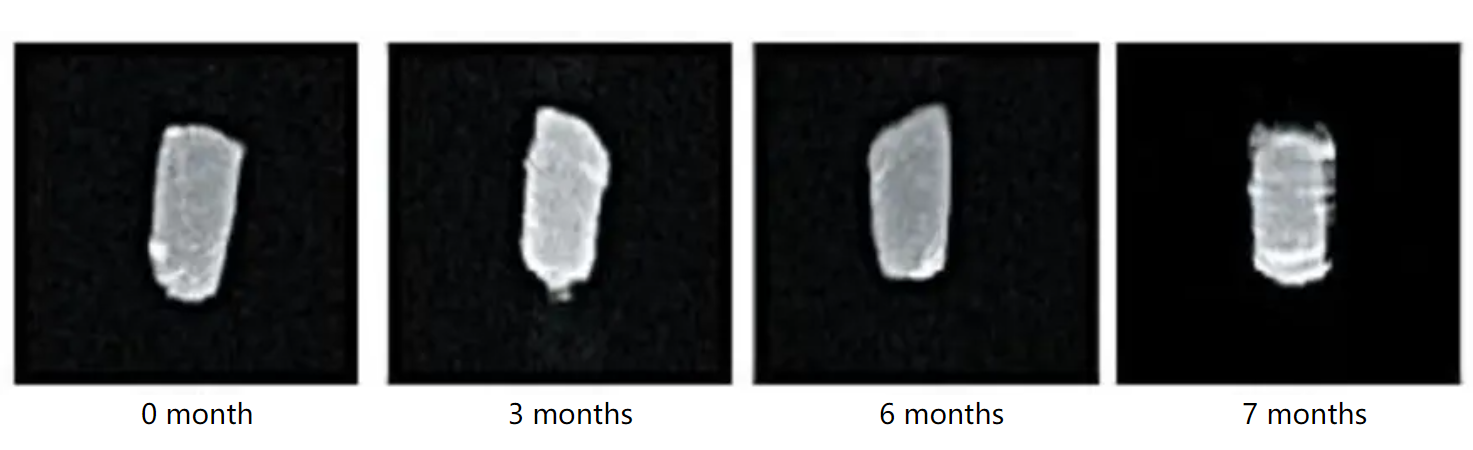
MRI of yak meat under different storage temperature and time
a: Storage under -10℃, MRI of yak meat at different storage times
b: Storage under -14℃, MRI of yak meat at different storage times
do: Storage under -18℃, MRI of yak meat at different storage times
d: Storage under -22℃, MRI of yak meat at different storage times
Referencia: Ma Ying, Yang Jumei, Wang Songlei, etc.. Analysis of moisture content changes in beef storage based on LF_NMR and imaging technology [j]. Food Industry Science and Technology, 2018,39(02):278-284.
 mohoso
mohoso