Pulsed NMR Advantages
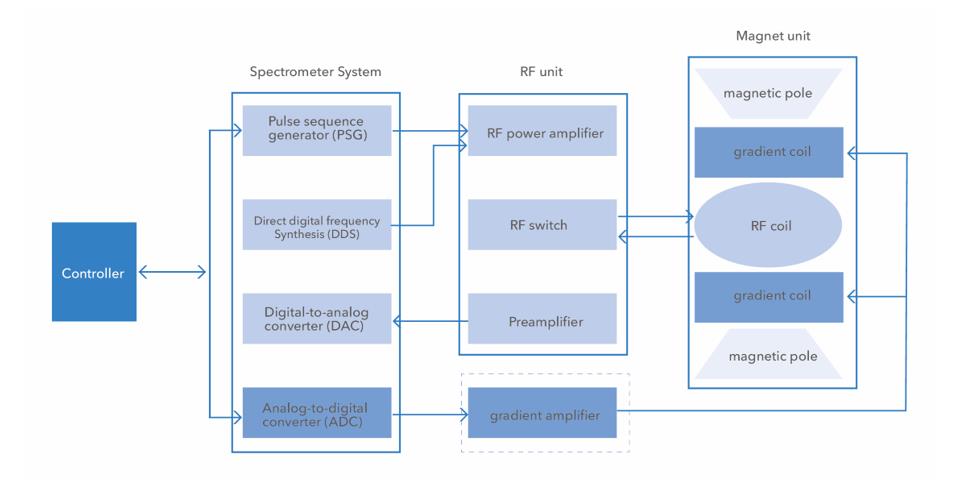
Pulsed NMR (Nuclear Magnetic Resonance) is a technique used in spectroscopy to study the structure and dynamics of molecules in solution. It works by exploiting the magnetic properties of atomic nuclei, specifically the behavior of their magnetic moments in an external magnetic field.
In pulsed NMR, a sample is placed in a strong, uniform magnetic field and exposed to a sequence of radiofrequency (RF) pulses. These pulses cause the magnetic moments of the nuclei in the sample to rotate or flip, which generates a signal that can be measured using a detector. The timing and duration of the RF pulses are carefully controlled to manipulate the nuclear spins and generate different types of signals.
The signals obtained from pulsed NMR experiments can provide a wealth of information about the molecular structure and properties of the sample. For example, by measuring the frequency of the signals, it is possible to determine the chemical composition of the sample. By analyzing the intensity and shape of the signals, it is possible to obtain information about the dynamics of the molecules in the sample, such as their motion and orientation.
Pulsed NMR is widely used in many fields of chemistry, biochemistry, and materials science, and is an important tool for studying the properties of complex molecules and materials.
| Pulsed NMR | Continuous wave NMR | Chemistry methods |
| Samples do not need baking. | Samples need baking about one hour | |
| Measuring time <1min, quick and suitable for mass detection | Measuring time <1min after baking | Several hours even more than ten hours |
| Deviation <1% | Deviation <1% | Deviation <2% |
| Non-destructive | Samples need baking | Destructive |
| Operation is simple | Operation is simple | Result is related to operator |
| Do not need special training. It only takes 10 min to do the operation | Do not need special training. It only take 10 min to do the operation | Need special training |
 NIUMAG
NIUMAG